NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 6 Science Chapter – 7 (Getting to Know Plants) has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter – 7 (Getting to Know Plants)
1. Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook.
(a) Stem absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Leaves hold the plant upright.
(c) Roots conduct water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and stamens in a flower is always equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are also joined together.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is joined to the petal.
Answer –
(a) Roots absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Stem holds the plant upright.
(c) Stems conduct water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and stamens in a flower may not be always equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are separate.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil may or may not be joined to the petal.
2. Draw
(a) a leaf,
(b) a taproot and
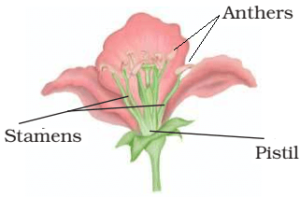
(c) a flower,
you have studied for Table 7.3
Answer –
(a)

Fig 7.1 – Leaf
(b)
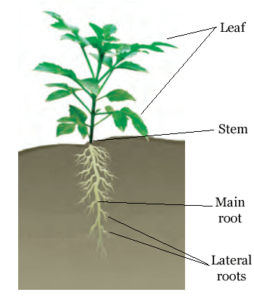
(c)
3. Can you find a plant in your house or in your neighborhood, which has a long but weak stem? Write its name. In which category will you place it?
Answer – Yes, money plant. It belongs to creepers.
4. What is the function of a stem?
Answer – A stem in a plant performs the following functions:
- The stem and its branches hold leaves to get maximum sunlight.
- It transports water from roots to different parts of the plant.
- It transports food from leaves to different parts of the plant.
- It bears leaves, flowers and fruits.
5. Which of the following leaves have reticulate venation?
Wheat, tulsi, maize, grass, coriander (dhania), China rose
Answer – Tulsi, China rose and coriander (dhania) have reticulate venation.
6. If a plant has fibrous root, what type of venation do its leaves have?
Answer – If a plant has fibrous root, its leaves have Parallel Venation.
7. If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have?
Answer – If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, it will have Tap root.
8. Is it possible for you to find out whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper?
Answer – Yes it is possible to find whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper.
9. What are the parts of a flower?
Answer – The names of various parts of a flower from outside to inside are:
(a) Sepals
(b) Petals
(c) Stamens
(d) Pistil
10. From the following plants, which of them have flowers?
Grass, maize, wheat, chilli, tomato, tulsi, peepal, shisham, banyan, mango, jamun, guava, pomegranate, papaya, banana, lemon, sugarcane, potato, groundnut
Answer –
| S.No | Name of the plant | Whether seen | Whether have flowers | |||
| Yes | No | |||||
| 1. | Grass | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 2. | Maize | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 3. | Wheat | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 4. | Chilli | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 5. | Tomato | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 6. | Tulsi | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 7. | Pipal | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 8. | Shisham | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 9. | Banyan | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 10. | Mango | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 11. | Jamun | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 12. | Guava | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 13. | Pomegranate | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 14. | Papaya | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 15. | Banana | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 16. | Lemon | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 17. | Sugarcane | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 18. | Potato | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 19. | Groundnut | Yes | ✓ | |||
11. Name the part of plant which produces food. Name the process.
Answer – Leaves produce food through a process called as Photosynthesis.
12. In which part of a flower, you will find the ovary?
Answer – Ovary is the lowermost part of the pistil.
13. Name two plants in which one has joined sepals and the other has separate sepals.
Answer –
Plants with joined sepals – Datura and Loki.
Plants with separate sepals – Rose and Gurhal.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science
- Chapter 1 – Food Where Does It Come From
- Chapter 2 – Components of Food
- Chapter 3 – Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 – Sorting Materials Into Groups
- Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances
- Chapter 6 – Changes Around Us
- Chapter 8 – Body Movements
- Chapter 9 – The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10 – Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11 – Light, Shadows and Reflection
- Chapter 12 – Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13 – Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14 – Water
- Chapter 15 – Air Around Us
- Chapter 16 – Garbage In, Garbage Out

Leave a Reply