NCERT Solutions Class 7 Mathematics
Chapter – 10 (Practical Geometry)
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 7 Mathematics Chapter – 10 Practical Geometry Exercise 10.2 has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter : 10 Practical Geometry
- NCERT Solution Class 7 Maths Exercise – 10.1
- NCERT Solution Class 7 Maths Exercise – 10.3
- NCERT Solution Class 7 Maths Exercise – 10.4
- NCERT Solution Class 7 Maths Exercise – 10.5
Exercise – 10.2
1. Construct ΔXYZ in which XY = 4.5 cm, YZ = 5 cm and ZX = 6 cm
Solution –
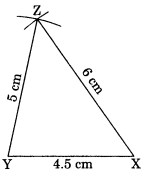
Steps of construction:
1. Draw a line segment XY = 4.5 cm.
2. With X as a center and radius 6 cm, draw an arc.
3. With Y as a center and radius 5 cm, draw another arc, cutting the previous arc at Z.
4. Join YZ and XZ.
Then, ΔXYZ is the required triangle.
2. Construct an equilateral triangle of side 5.5 cm.
Solution –
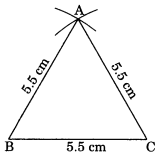
Steps of construction:
1. Draw a line segment BC = 5.5 cm.
2. With B as a center and radius 5.5 cm, draw an arc.
3. With C as a center and radius 5.5 cm, draw another arc, cutting the previous arc at A.
4. Join BA and CA.
Then, ΔABC is the required equilateral triangle.
3. Draw ΔPQR with PQ = 4 cm, QR = 3.5 cm and PR = 4 cm. What type of triangle is this?
Solution –
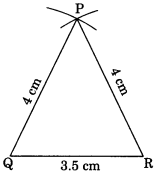
Steps of construction:
1. Draw a line segment QR = 3.5 cm.
2. With Q as a center and radius 4 cm, draw an arc.
3. With R as a center and radius 4 cm, draw another arc, cutting the previous arc at P.
4. Join PQ and PR.
Then, ΔPQR is the required isosceles triangle.
4. Construct ΔABC such that AB = 2.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 6.5 cm. Measure ∠B.
Solution –
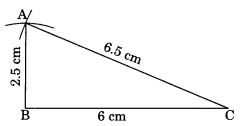
Steps of construction:
1. Draw a line segment BC = 6 cm.
2. With B as a center and radius 2.5 cm, draw an arc.
3. With C as a center and radius 6.5 cm, draw another arc, cutting the previous arc at A.
4. Join AB and AC.
Then, ΔABC is the required triangle.
5. When we measure the angle B of triangle by protractor, then angle is equal to ∠B = 90o

Leave a Reply