NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
Chapter – 14 (Practical Geometry)
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 6 Mathematics Chapter – 14 Practical Geometry Exercise 14.4 has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter 14: Practical Geometry
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Maths Exercise – 14.1
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Maths Exercise – 14.2
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Maths Exercise – 14.3
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Maths Exercise – 14.5
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Maths Exercise – 14.6
Exercise – 14.4
1. Draw any line segment . Mark any point M on it. Through M, draw a perpendicular to
. (use ruler and compasses)
Solutions :
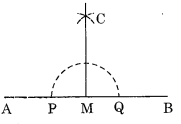
Step 1: Draw a line segment and mark any point M on it.
Step 2: Put the pointer of the compass at M and draw an arc of suitable radius such that it intersects at P and Q.
Step 3: Take P and Q as centres and radius greater than PM, draw two arcs such that they intersect each other at C.
Step 4: Join M and C.
Thus CM is the perpendicular to .
2. Draw any line segment . Take any point R not on it. Through R, draw a perpendicular to
. (Use ruler and set square).
Solutions:
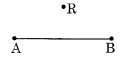
Step 1: Draw a line segment and a point R outside of
.
Step 2: Place a set square on such that one side of its right angle be along it.
Step 3: Place a ruler along the longer side of the set square.
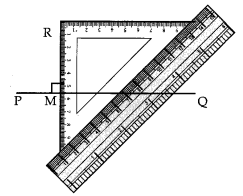
Step 4: Hold the ruler fix and slide the set square along the ruler till it touches the point R.
Step 5: Join RM along the edge through R.
Thus ⊥
.
3. Draw a line l and a point X on it. Through X, draw a line segment perpendicular to l. Now draw a perpendicular to
at y. (Use ruler and compasses)
Solutions:
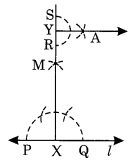
Step 1: Draw a line l and take a point X on it.
Step 2: Draw an arc with centre X and of suitable radius to intersect the line l at two points P and Q.
Step 3: With P and Q as centres and a radius greater than P draw two arcs to intersect each other at M.
Step 4: Join XM and produce to Y.
Step 5: With Y as centre and a suitable radius, draw an arc to intersect XY at two points R and S.
Step 6: With R and S as centres and a radius greater than YR, draw two arcs to intersect each other at A.
Step 7: Join Y and A.
Thus ⊥
.

Leave a Reply