NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
Chapter – 13 (Surface Areas and Volumes)
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter – 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 13.5 has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter : 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 13.1
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 13.2
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 13.3
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 13.4
Exercise – 13.5
1. A copper wire, 3 mm in diameter, is wound about a cylinder whose length is 12 cm, and diameter 10 cm, so as to cover the curved surface of the cylinder. Find the length and mass of the wire, assuming the density of copper to be 8.88 g per cm3.
Solution – A figure is drawn to visualize the cylinder.
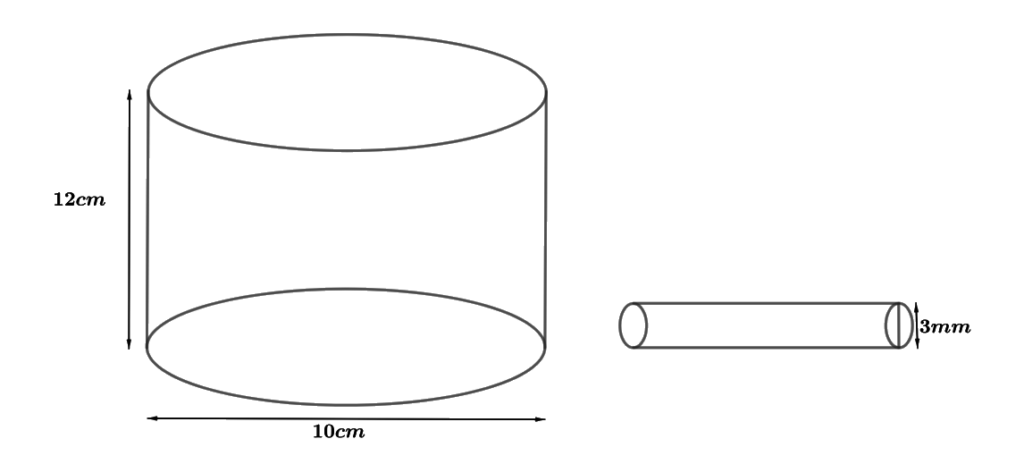
Diameter of cylinder = 10 cm
So, the radius of the cylinder (r) = 10/2 cm = 5 cm
∴ Length of wire in completely one round = 2πr = 3.14 × 5 cm = 31.4 cm
Diameter of wire = 3 mm = 3/10 cm
∴ The thickness of the cylinder covered in one round = 3/10 m
Hence, the number of turns (rounds) of the wire to cover 12 cm will be =
= 40
Now, the length of wire required to cover the whole surface = length of wire required to complete 40 rounds = 40 × 31.4 cm
= 1256 cm
Radius of the wire = 0.3/2 = 0.15 cm
The volume of wire = Area of the cross-section of wire × Length of wire
= π(0.15)2 × 1257.14
= 88.898 cm3
We know,
Mass = Volume × Density
= 88.898 × 8.88
= 789.41 gm
Thus, the length of the wire is 12.57 m and the mass is 790 g (approx.)
2. A right triangle whose sides are 3 cm and 4 cm (other than the hypotenuse) is made to revolve about its hypotenuse. Find the volume and surface area of the double cone so formed. (Choose the value of π as found appropriate)
Solution – Draw the diagram as follows:
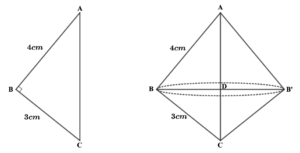
From the figure it can be seen that BD ⊥ AC
In ΔABC right-angled at B using Pythagoras theorem,
AC² = AB² + BC²
AC = (3 cm)² + (4 cm)²
⇒ AC = 9 cm² + 16 cm²
⇒ AC = 25 cm²
⇒ AC = 5 cm
Consider ΔABC and ΔBDC
∠ABC = ∠CDB = 90° (BD ⊥ AC)
∠BCA = ∠BCD (common)
By AA criterion of similarity ΔABC ∼ ΔBDC
Therefore,
AB/BD = AC/BC (Corresponding sides of similar triangles are in proportion)
BD = (AB × BC)/AC
= (3 cm × 4 cm)/5 cm
= 12/5 cm
= 2.4 cm
We know that, Volume of the cone = 1/3πr²h
Volume of double cone = Volume of Cone ABB’ + Volume of Cone BCB’
= 1/3 × π(BD)² × AD + 1/3π (BD)² × DC
= 1/3 × π(BD)² [AD + DC]
= 1/3 × π(BD)² × AC
= 1/3 × 3.14 × 2.4 cm × 2.4 cm × 5 cm
= 30.144 cm³
We know that, CSA of frustum of a cone = πrl
CSA of double Cone = CSA of cone ABB’ + CSA of cone BCB’
= π × BD × AB + π × BD × BC
= π × BD [ AB + BC]
= 3.14 × 2.4 cm × [3 cm + 4 cm]
= 3.14 × 2.4 cm × 7 cm
= 52.752 cm²
= 52.75 cm²
3. A cistern, internally measuring 150 cm × 120 cm × 100 cm, has 129600 cm3 of water in it. Porous bricks are placed in the water until the cistern is full to the brim. Each brick absorbs one-seventeenth of its own volume of water. How many bricks can be put in without overflowing the water, each being 22.5 cm × 7.5 cm × 6.5 cm?
Solution – Let’s construct a diagram according to the given question.
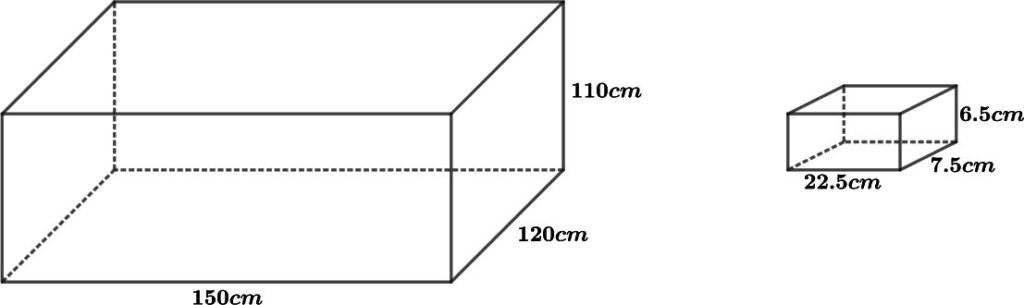
Given that the dimension of the cistern = 150 × 120 × 110
So, volume = 1980000 cm3
Volume to be filled in cistern = 1980000 – 129600
= 1850400 cm3
Now, let the number of bricks placed to be “n”
So, the volume of n bricks will be = n×22.5×7.5×6.5
Now, as each brick absorbs one-seventeenth of its volume, the volume will be
= n/(17)×(22.5×7.5×6.5)
For the condition given in the question,
The volume of n bricks has to be equal to the volume absorbed by n bricks + the volume to be filled in the cistern
1980000 cm³ = 129600 cm³ + 16/17 × n × 1096.875 cm³
n = [(1980000 cm³ – 129600 cm³) × 17] / (16 × 1096.875) cm³
= (1850400 cm³ × 17) / (16 × 1096.875 cm³)
= 1792.41
4. In one fortnight of a given month, there was a rainfall of 10 cm in a river valley. If the area of the valley is 7280 km2, show that the total rainfall was approximately equivalent to the addition to the normal water of three rivers, each 1072 km long, 75 m wide and 3 m deep.
Solution – From the question, it is clear that
Volume of the rainfall = Area of the river valley × height of rainfall in the river valley
Volume of the river = length × breadth × height [Assuming the river valley to be cuboidal]
Area of the valley, A = 7280 km² = 7280 × 1000000 m² = 7.28 × 109 m²
Height of rainfall in a fortnight, h = 10 cm = 10/100 m = 0.1 m
Volume of the rainfall = Area of the river valley × height of rainfall in the river valley
= 7.28 × 109 m² × 0.1 m
= 7.28 × 108 m³
Length of river, l = 1072 km = 1072 × 1000 m = 1.072 × 106 m
Width of river, b = 75 m
Depth of river, h = 3 m
Volume of 3 rivers = 3 × volume of one river
= 3 lbh
= 3 × 1.072 × 106 m × 75 m × 3 m
= 723.6 × 106 m³
= 7.236 × 108 m³
Since 7.236 × 108 m³ is approximately equivalent to 7.28 × 108 m³, therefore, we can say that total rainfall in the valley was approximately equivalent to the addition of normal water of three rivers each 1072 km long, 75 m wide and 3 m deep.
5. An oil funnel made of a tin sheet consists of a 10 cm long cylindrical portion attached to a frustum of a cone. If the total height is 22 cm, the diameter of the cylindrical portion is 8 cm, and the diameter of the top of the funnel is 18 cm, find the area of the tin sheet required to make the funnel (see Fig.).
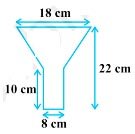
Solution – Given
Diameter of the upper circular end of the frustum part = 18 cm
radius (r1) = 9 cm
the radius of the lower circular end of the frustum (r2) will be equal to the radius of the circular end of the cylinder
r2 = 8/2 = 4 cm
Now, height (h1) of the frustum section = 22 – 10 = 12 cm
Height (h2) of cylindrical section = 10 cm (given)
Now, the slant height will be l = = √h12 + (r1 – r2)2
= √(12)² + (9 – 4)²
= √144 + 25
= √169 cm²
= 13 cm
Area of tin sheet required = CSA of frustum part + CSA of the cylindrical part
= π (r1 + r2)l + 2πr2h
= 22/7 [(9 + 4) × 13 + 2 × 4 × 10]
= 22/7 [169 + 80]
= 22/7 × 249
= 5478/7
= 782.57 cm²
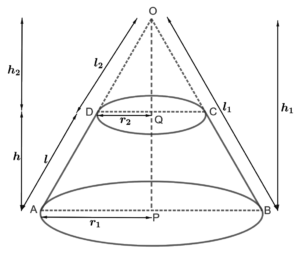
6. Derive the formula for the curved surface area and total surface area of the frustum of a cone, given to you in Section 13.5, using the symbols as explained.
Solution – Consider a frustum of a cone with h as height, l as the slant height, r1 and r2 as radii of the ends where r1 > r2.
To Prove:
(i) CSA of the frustum of the cone = πl (r1 + r2)
(ii) TSA of the frustum of the cone = πl (r1 + r2) + πr1² + πr2²
where r1, r2, h and l are the radii height and slant height of the frustum of the cone respectively.
Construction:
Extended side BC and AD of the frustum of cone to meet at O
Proof :
The frustum of a cone can be viewed as a difference of two right circular cones OAB and OCD.
Let h1 and l1 be the height and slant height of cone OAB and h2 and l2 be the height and slant height of cone OCD respectively.
In ΔAPO and ΔDQO
∠APO = ∠DQO = 90° (Since both cones are right circular cones)
∠AOP = ∠DOQ (Common)
Therefore, ΔAPO ∼ ΔDQO (AA criterion of similarity)
AP/DQ = AO/DO = OP/OQ (Corresponding sides of similar triangles are proportional)
⇒ r1/r2 = l1/l2 = h1/h2
⇒ r1/r2 = l1/l2 or ⇒ r2/r1 = l2/l1
Subtracting 1 from both sides we get
r1/r2 – 1 = l1/l2 – 1
(r1 – r2)/r2 = (l1 – l2) / l2
(r1 – r2)/r2 = l/l2 [From diagram, l1 – l2 = l]
l2 = lr2/(r1 – r2) —————– (i)
r2 / r1 = l2 / l1
Subtracting 1 from both sides we get
r2 / r1 – 1 = l2 / l1 – 1
(r2 – r1) / r1 = (l2 – l1) / l1
(r1 – r2) / r1 = (l1 – l2) / l1
(r1 – r2) / r1 = l / l1
l1 = lr1/(r1 – r2) —————- (ii)
(i) CSA of frustum of cone = CSA of cone OAB – CSA of cone OCD
= πr1l1 – πr2l2
= π (r1l1 – r2l2)
= π [(r1 × lr1/(r1 – r2) – r2 × lr2/(r1 – r2)] [Using (i) and (ii)]
= π [(lr1² – lr2²)/(r1 – r2)]
= π [l(r12 – r22)/(r1 – r2)]
= π [l(r1 – r2)(r1 + r2)/(r1 – r2)] [Since, a² – b² = (a – b)(a + b)]
= π l(r1 + r2)
TSA of frustum of cone = CSA of frustum + Area of lower circular end + Area of top circular end
= πl (r1 + r2) + πr1² + πr1²
Therefore, CSA of the frustum of the cone = πl (r1 + r2)
TSA of the frustum of the cone = πl (r1 + r2) + πr1² + πr2²
Hence Proved.
7. Derive the formula for the volume of the frustum of a cone.
Solution – Consider the same diagram as the previous question.

To Prove:
CSA of the frustum of the cone = 1/3πh (r12 + r22 + r1r2)
where r1, r2, and h are the radii and height of the frustum of the cone respectively.
Proof :
The frustum of a cone can be viewed as a difference of two right circular cones OAB and OCD.
Let h1 and l1 be the height and slant height of cone OAB and h₂ and l₂ be the height and slant height of cone OCD respectively.
In ΔAPO and ΔDQO
∠APO = ∠DQO = 90° (Since both cones are right circular cones)
∠AOP = ∠DOQ (Common)
Therefore, ΔAPO ∼ ΔDQO ( A.A criterion of similarity)
AP/DQ = AO/DO = OP/OQ (Corresponding sides of similar triangles are proportional)
⇒ r1/r1 = l1/l2 = h1/h2
⇒ r1/r1 = h1/h2
or
⇒ r2/r1 = h2/h1
Subtracting 1 from both sides
r1/r2 – 1 = h1/h2 – 1
(r1 – r2)/r2 = (h1 – h2)/h2
(r1 – r2)/r2 = h/h2 [From figure h1 – h2 = h]
h2 = hr2/(r1 – r2) —————— (ii)
Now, considering r2/r1 = h2/h1
Subtracting 1 from both sides we get
r2/r1 – 1 = h2/h1 – 1
(r2 – r1)/r1 = (h2 – h1)/h1
(r1 – r2)/r1 = (h1 – h2)/h1
(r1 – r2)/r1 = h/h1
h1 = hr1/(r1 – r2) —————— (ii)
Volume of frustum of cone = Volume of cone OAB – Volume of cone OCD
= 1/3 πr12h1 – 1/3 πr22h2
= 1/3π [r12h1 – r22h2]
= 1/3π [r12 × hr1/(r1 – r2) – r22 × hr2(r1 – r2)] [Using (i) and (ii)]
= 1/3π [hr13/(r1 – r2) – hr23/(r1 – r2)]
= 1/3πh [(r13 – r23)/(r1 – r2)]
= 1/3πh [(r1 – r2)(r12 + r1r2 + r22)/(r1 – r2)] [Since, (a³ – b³) = (a – b)(a² + ab + b²)]
= 1/3πh (r1² + r2² + r1r2)
Hence proved, volume of the frustum = 1/3πh (r1² + r2² + r1r2)

Leave a Reply