NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
Chapter – 12 (Areas Related to Circles)
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter – 12 Areas Related to Circles Exercise 12.2 has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter : 12 Areas Related to Circles
Exercise – 12.2
Unless stated otherwise, use π =22/7.
1. Find the area of a sector of a circle with a radius 6 cm if the angle of the sector is 60°.
Solution – Area of the sector making angle θ = (θ/360°) × π r2
Area of the sector making angle 60° = (60°/360°) × π r2 cm2
= (1/6) × 62π
= 36/6 π cm2
= 6 × 22/7 cm2
= 132/7 cm2
2. Find the area of a quadrant of a circle whose circumference is 22 cm.
Solution – Quadrant of a circle means sector is making angle 90°.
Circumference of the circle = 2πr = 22 cm
Radius of the circle = r = 22/2π cm = 7/2 cm
Area of the sector making angle 90° = (90°/360°) × π r2 cm2
= (1/4) × (7/2)2π
= (49/16) π cm2
= (49/16) × (22/7) cm2
= 77/8 cm2
= 9.6 cm2
3. The length of the minute hand of a clock is 14 cm. Find the area swept by the minute hand in 5 minutes.
Solution – Minute hand of clock acts as radius of the circle.
∴ Radius of the circle (r) = 14 cm
Angle rotated by minute hand in 1 hour = 360°
∴ Angle rotated by minute hand in 5 minutes = 360° × 5/60 = 30°
Area of the sector making angle 30° = (30°/360°) × π r2 cm2
= (1/12) × 142π
= 196/12 π cm2
= (49/3) × (22/7) cm2
= 154/3 cm2
Area swept by the minute hand in 5 minutes = 154/3 cm2
4. A chord of a circle of radius 10 cm subtends a right angle at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding:
(i) minor segment
(ii) major sector. (Use π = 3.14)
Solution – In a circle with radius r and the angle at the centre with degree measure θ
(i) Area of the sector = θ/360° × πr2
(ii) Area of the segment = Area of the sector – Area of the corresponding triangle
Area of the right triangle = 1/2 × base × height
Let’s draw a figure to visualize the area to be calculated.
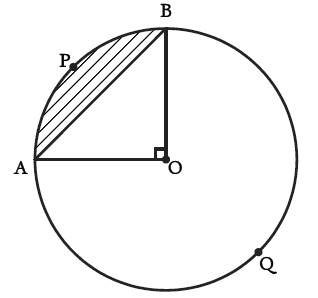
Here, Radius, r = 10 cm, θ = 90°
Visually it’s clear from the figure that,
AB is the chord that subtends a right angle at the centre.
(i) Area of minor segment APB = Area of sector OAPB – Area of right triangle AOB
(ii) Area of major segment AQB = πr² – Area of minor segment APB
Area of the right triangle ΔAOB = 1/2 × OA × OB
(i) Area of minor segment APB = Area of sector OAPB – Area of right ΔAOB
= θ/360° × πr2 – 1/2 × OA × OB
= 90°/360° × πr2 – 1/2 × r × r
= 1/4 πr2 -1/2r2
= r2 (1/4 π – 1/2)
= r2 (3.14 – 2)/4
= (r2 × 1.14)/4
= (10 × 10 × 1.14)/4 cm² (Since radius r is given as 10 cm)
= 28.5 cm²
(ii) Area of major sector AOBQ = πr2 – Area of minor sector OAPB
= πr2 – θ/360° × πr2
= πr2 (1 – 90°/360°)
= 3.14 × (10 cm)2 × 3/4
= 235.5 cm2
5. In a circle of radius 21 cm, an arc subtends an angle of 60° at the centre. Find:
(i) the length of the arc
(ii) area of the sector formed by the arc
(iii) area of the segment formed by the corresponding chord
Solution – Let’s draw a figure to visualize the problem.
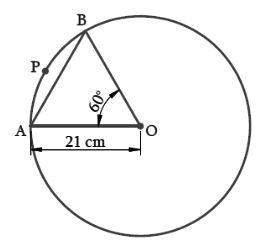
Here, r = 21 cm, θ = 60°
Visually it’s clear from the figure that,
Area of the segment APB = Area of sector AOPB – Area of ΔAOB
(i) Length of the Arc, APB = θ/360° × 2πr
= 60°/360° × 2 × 22/7 × 21 cm
= 22 cm
(ii) Area of the sector, AOBP = θ/360° × πr2
= 60°/360° × 22/7 × 21 × 21 cm2
= 231 cm2
(iii) Area of the segment = Area of the sector AOBP – Area of the triangle AOB
To find the area of the segment, we need to find the area of ΔAOB
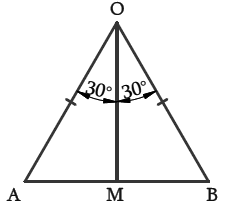
In ΔAOB, draw OM ⊥ AB.
Consider ΔOAM and ΔOMB,
OA = OB (radii of the circle)
OM = OM (common side)
∠OMA = ∠OMB = 90° (Since OM ⊥ AB)
Therefore, ΔOMB ≅ ΔOMA (By RHS Congruency)
So, AM = MB (Corresponding parts of the congruent triangles are always equal)
∠AOM = ∠BOM = 1/2 × 60° = 30°
In ΔAOM,
cos 30° = OM/OA and sin 30° = AM/OA
√3/2 = OM/r and 1/2 = AM/r
OM = (√3/2) r and AM = (1/2) r
AB = 2AM
AB = 2 × (1/2) r
AB = r
Therefore, area of ΔAOB = 1/2 × AB × OM
= 1/2 × r × (√3/2) r
= 1/2 × 21 cm × (√3/2) × 21 cm
= 441√3/4 cm2
Area of the segment formed by the chord = Area of the sector AOBP – Area of the triangle AOB
= (231 – 441√3/4) cm2
6. A chord of a circle of radius 15 cm subtends an angle of 60° at the centre. Find the areas of the corresponding minor and major segments of the circle. (Use π = 3.14 and √3 = 1.73)
Solution –
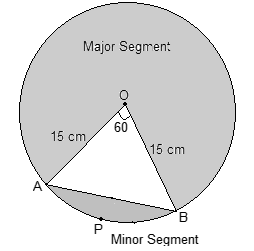
Given – Radius of the circle = 15 cm
θ = 60°
So,
The area of sector OAPB = (60°/360°) × πr2 cm2
= 225/6 π cm2
Now, ΔAOB is equilateral because two sides are circle radii and hence equal, and one angle is 60°.
Alternatively, the area of ΔAOB = (√3/4) × a2
= (√3/4) × 152
= 97.31 cm2
Therefore, the area of ΔAOB = 97.31 cm2
Now, Area of OAPB – Area of ΔAOB = Area of minor segment APB
Alternatively, the area of minor segment APB = ((225/6)π – 97.31) cm2
= 225/6 × 3.14 – 97.31 cm2
= 117.75 – 97.31 cm2
= 20.43 cm2
Area of circle – Area of segment APB = Area of major segment
Alternatively, the area of major segment = (π × 152) – 20.4
= 3.14 × 225 – 20.4 cm2
= 706.5 – 20.4 cm2
= 686.06 cm2
7. A chord of a circle of radius 12 cm subtends an angle of 120° at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding segment of the circle. (Use π = 3.14 and √3 = 1.73)
Solution –
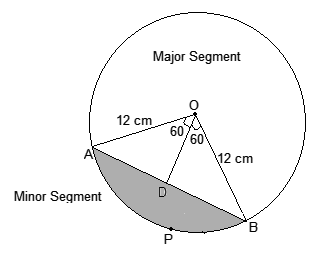
Given – Radius, r = 12 cm
Draw a perpendicular OD on chord AB now, and it will bisect the chord AB.
So, AD = DB
Now, the area of the minor sector = (θ/360°) × πr2
= (120/360) × 3.14 × 122
= 1/3 × 3.14 × 144
= 150.72 cm2
Now, considering the ΔAOB,
∠ OAB = 180° – (90° + 60°)
= 30°
Now, cos 30° = AD/OA
√3/2 = AD/12
AD = 6√3 cm
We know that OD bisects AB .
So, AB = 2 × AD = 12√3 cm
As a result, sin 30° = OD/OA
Or,
½ = OD/12
Therefore, OD = 6 cm
Alternatively, the area of ΔAOB = ½ × base × height
Base = AB = 12√3 and
Here, height = OD = 6
Alternatively, the area of ΔAOB = ½ × 12√3 × 6
= 36√3 cm2
= 36 × 1.73 cm2
= 62.28 cm2
Therefore, area of the Minor sector – area of ΔAOB = Area of the corresponding Minor segment
= 150.72 cm2– 62.28 cm2
= 88.44 cm2
8. A horse is tied to a peg at one corner of a square-shaped grass field of side 15 m by means of a 5 m long rope (see Fig. 12.11). Find
(i) the area of that part of the field in which the horse can graze.
(ii) the increase in the grazing area if the rope were 10 m long instead of 5 m. (Use π = 3.14)
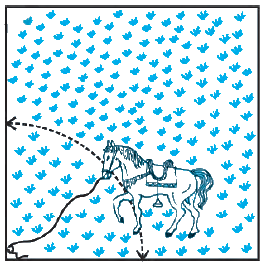
Solution – As the horse is tied at one end of a square field, it will graze only a quarter (i.e. sector with θ = 90°) of the field with a radius 5 m.
(i) From the figure it’s clear that the horse can graze an area of a sector of a circle with radius (r) 5m and an angle with a degree measure 90° [Since its a square field]
Length of the rope = 5 m
Area of the field the horse can graze = Area of the sector with θ = 90° and r = 5
= θ/360° × πr2
= 90°/360° × πr2
= 1/4 × π × (5 m)2
= 25/4 × 3.14 m2
= 19.625 m2
(ii) The area that can be grazed by the horse when the length of the rope is 10m, is the area of the sector of a circle with a radius (r) 10 m and an angle with a degree measure 90°.
Area of the field the horse can graze = Area of the sector with θ = 90° and r = 10
= 90°/360° × πr2
= 1/4 × 3.14 × 100 m2
= 78.5 m2
Increase in the grazing area
= 78.5 m2 – 19.625 m2
= 58.875 m2
9. A brooch is made with silver wire in the form of a circle with a diameter 35 mm. The wire is also used in making 5 diameters which divide the circle into 10 equal sectors, as shown in Fig. 12.12. Find:
(i) the total length of the silver wire required.
(ii) the area of each sector of the brooch.
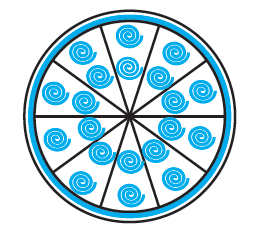
Solution –
(i) Diameter of the brooch (d) = 35 mm
Total length of silver wire required = circumference of brooch + 5 × diameter
= πd + 5d
= (π + 5) × 35
= (22/7 + 5) × 35
= (22 + 35)/7 × 35
= 57 × 5
= 285 mm
(ii) Radius of the brooch (r) = 35/2 mm
The wire divides the brooch into 10 equal sectors.
So, angle of the sector (θ) = 360°/10 = 36°
∴ Area of each sector of the brooch = 36°/360° × πr2
= 1/10 × 22/7 × 35/2 mm × 35/2 mm
= 96.25 mm2
10. An umbrella has 8 ribs which are equally spaced (see Fig. 12.13). Assuming the umbrella to be a flat circle of radius 45 cm, find the area between the two consecutive ribs of the umbrella.
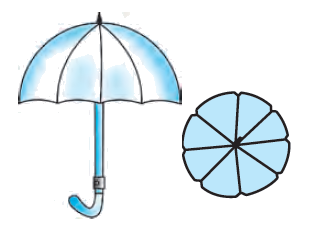
Solution – There are 8 equally spaced ribs in an umbrella, so the umbrella is assumed to be a flat circle.
∴ The angle between 2 consecutive ribs (θ) = 360°/8 = 45°
The radius of the flat circle (r) is given as 45 cm.
The area between 2 consecutive ribs of the umbrella = Area of a sector with an angle of 45° = θ/360° × πr2
= 45°/360° × 22/7 × 45 cm × 45 cm
= 1/8 × 22/7 × 45 cm × 45 cm
= 22275/28 cm2
= 795.535 cm2
11. A car has two wipers which do not overlap. Each wiper has a blade of length 25 cm sweeping through an angle of 115°. Find the total area cleaned at each sweep of the blades.
Solution – Let’s draw a figure according to the given question.
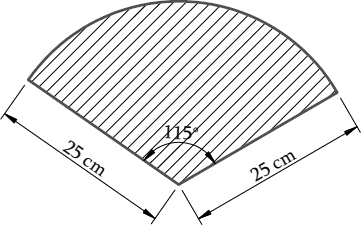
Given,
Radius (r) = 25 cm
Sector angle (θ) = 115°
Since there are 2 blades,
The total area of the sector made by wiper = 2 × (θ/360°) × π r2
= 2 × (115/360) × (22/7) × 252
= 2 × 158125/252 cm2
= 158125/126 = 1254.96 cm2
12. To warn ships of underwater rocks, a lighthouse spreads a red-coloured light over a sector of angle 80° to a distance of 16.5 km. Find the area of the sea over which the ships are warned. (Use π = 3.14)
Solution – The lighthouse spreads red coloured light over a sector of a circle with a radius 16.5 km and an angle of degree measure 80°
Area of the sea over which the ships are warned = Area of the sector of the circle with radius 16.5 km with an angle of degree measure 80°
= θ/360° × πr2
= 80°/360° × πr2
= 2/9πr2
= 2/9 × 3.14 × 16.5 km × 16.5 km
= 189.97 km2
13. A round table cover has six equal designs, as shown in Fig. 12.14. If the radius of the cover is 28 cm, find the cost of making the designs at the rate of ₹ 0.35 per cm2. (Use √3 = 1.7)
Solution –
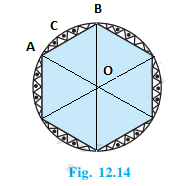
Total number of equal designs = 6
AOB= 360°/6 = 60°
The radius of the cover = 28 cm
Cost of making design = ₹ 0.35 per cm2
Since the two arms of the triangle are the radii of the circle and thus are equal, and one angle is 60°, ΔAOB is an equilateral triangle. So, its area will be (√3/4) × a2 sq. units
Here, a = OA
∴ Area of equilateral ΔAOB = (√3/4) × 282
= 1.7 / 4 × 28 × 28
= 333.2 cm2
Area of sector ACB = (60°/360°) × πr2 cm2
= 1/6 × 3.14 × 28 × 28
= 410.66 cm2
So, the area of a single design = the area of sector ACB – the area of ΔAOB
= 410.66 cm2 – 333.2 cm2
= 77.46 cm2
∴ area of 6 designs = 6 × 77.46 cm2
= 464.76 cm2
So, total cost of making design = 464.76 cm2 × Rs.0.35 per cm2
= Rs. 162.66
14. Tick the correct solution in the following:
The area of a sector of angle p (in degrees) of a circle with radius R is
(A) p/180 × 2πR
(B) p/180 × π R2
(C) p/360 × 2πR
(D) p/720 × 2πR2
Solution – The area of a sector = (θ/360°) × πr2
Given, θ = p
So, the area of sector = p/360 × πR2
Multiplying and dividing by 2 simultaneously,
= (p/360) × 2/2 × πR2
= (p/360) × πR2
= (p/720) × 2πR2
So, option (D) is correct.
Go Back To Chapters

Leave a Reply