NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 9 Science Chapter – 5 (The Fundamental Unit of Life) has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter – 5 (The Fundamental Unit of Life)
Questions
1. Who discovered cells, and how?
Answer – Cell was discovered by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke in 1665. He used self-designed microscope to observe cells in a cork slice back then.
2. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer – Cells are called the structural and functional unit of life because all the living organisms are made up of cells and all the functions that take place inside the organisms are performed by cells.
Questions
1. How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer – CO2 moves in and out of the cells by the process of diffusion which involves the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration across the cell membrane.
Water moves in and out of the cells by osmosis which involves the movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from a solution of lower concentration of solutes to higher concentration of solutes to which the membrane is relatively impermeable.
2. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer – Plasma membrane is called selectively permeable membrane because it allows or permits the entry and exit of some selected substances across it and not all of them.
Questions
1. Fill in the gaps in the following table, illustrating the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| 1. Size: generally small ( 1-10 µm) 1 µm= 10-6 m | 1. Size: generally large (5-100 µm) |
| 2. Nuclear region: ________ and is known as ________ . | 2. Nuclear region: well-defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane |
| 3. Chromosome: single | 3. More than one chromosome |
| 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles are absent | 4. _____________ . |
Answer –
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| 1. Size: generally small ( 1-10 µm) 1 µm = 10-6 m | 1. Size: generally large (5-100 µm) |
| 2. Nuclear region: poorly defined because of the absence of a nuclear membrane, and is known as nucleoid | 2. Nuclear region: well-defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane |
| 3. Chromosome: single | 3. More than one chromosome |
| 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles are absent | 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, plastids, etc., are present. |
Questions
1. Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer – Mitochondria and plastids their own genetic material
2. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer – In the event of any damage to cells and when the revival of cells is not possible, Lysosomes burst, and enzymes digest such cells. This is why lysosomes are often referred to as ‘suicide bags’.
3. Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer – Lysosomes are called suicide bags because in case of disturbance of their cellular metabolism they digest their own cell by releasing own enzymes.
4. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer – The proteins are synthesised in the ribosomes that are also known as protein factories.
Exercises
1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer – The following table depicts the differences between plant cells and animal cells.
| Animal cell | Plant cell |
| Has a cell wall. | Has cell wall made up of cellulose. |
| It does not contain chloroplast. | It contains chloroplast. |
| It has centrosome. | It does not has centrosome. |
| Vacuoles are smaller in size. | Vacuoles are larger in size. |
| Lysosomes are larger in number. | Lysosomes are absent or very few in number |
| Prominent Golgi bodies are present. | Subunits of Golgi bodies are present. |
2. How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer – The following are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| Most prokaryotes are unicellular. | Most eukaryotes are multi-cellular. |
| Size of the cell – (0.5- 5 μ). | Size of the cell – (50- 100 μ). |
| It contains a single chromosome. | It contains more than one chromosome. |
| Nucleolus is absent. | Nucleolus is present. |
| Membrane-bound cell organelles such as plastids, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, etc. are absent. | Cell organelles such as mitochondria, plastids, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, etc. are present. |
| Cell division occurs through binary fission | Cell division occurs by mitosis. |
3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer – Plasma membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell by diffusion or osmosis. Thus, if the plasma membrane is ruptured, the cell contents might leak out and cell will die.
4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer – Golgi apparatus has the function of storage modification and packaging of the products. If there is no Golgi apparatus then the packaging and transporting of materials synthesized by cell will not happen.
5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer – Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of cells because energy required for various chemical activities needed for life is released by mitochondria in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) molecules.
6. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer – Lipids and proteins are synthesised in the ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum).
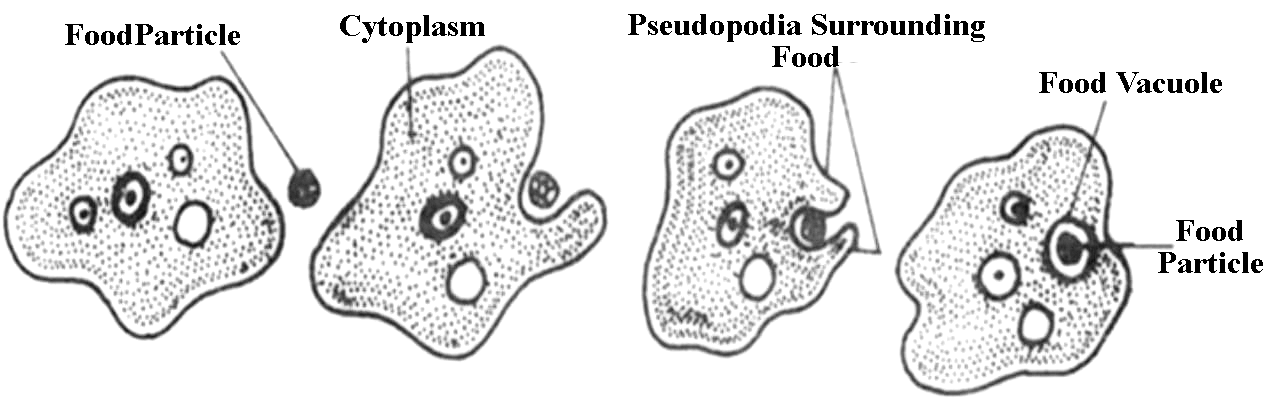
7. How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer – Amoeba obtain its food through the process of endocytosis. The plasma membrane of Amoeba is flexible which help to engulf its food particles and other material from its external environment.
8. What is osmosis?
Answer – Osmosis is the process in which water molecules moves from the region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a semi permeable membrane.
9. Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed-out portions of A and D.
Answer –
(i) Water accumulates in the hollowed portions of B and C as a difference in the water concentration is observed. Thereby, endosmosis occurs as the cells act as a semipermeable membrane.
(ii) Potato A is essential in this experiment as it is significant to compare different scenarios seen in potato cups B, C and D. Potato A in this experiment clearly shows that the potato cavity on its own cannot bring about water movement.
(iii) Cup in A does not show any change in the water flow concentration for osmosis to occur, which requires concentration to be higher than the other. Cells in cup D are dead; thus, there is no existence of a semipermeable membrane for water flow. Consequently, osmosis does not occur.
10. Which type of cell division is required for the growth and repair of the body, and which type is involved in the formation of gametes?
Answer – There are two ways in which a cell divides:
- Mitosis
- Meiosis
Mitosis is the type of cell division that is involved in the growth and repair of the body, whereas meiosis is a type of cell division which results in the formation of gametes.

Leave a Reply