NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science (Civics – Social and Political Life – III)
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 8 Social Science (Civics – Social and Political Life – III) Chapter – 5 (Judiciary) has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Civics (Social and Political Life – III)
- Chapter – 1 — The Indian Constitution
- Chapter – 2 — Understanding Secularism
- Chapter – 3 — Why Do We Need A Parliament?
- Chapter – 4 — Understanding Laws
- Chapter – 6 — Understanding Our Criminal Justice System
- Chapter – 7 — Understanding Marginalisation
- Chapter – 8 — Confronting Marginalisation
- Chapter – 9 — Public Facilities
- Chapter – 10 — Law and Social Justice
Chapter – 5 (Judiciary)
1. You read that one of the main functions of the judiciary is ‘upholding the law and enforcing Fundamental Rights’. Why do you think an independent judiciary is necessary to carry out this important function?
Answer – An independent judiciary is necessary to carry out the function of ‘upholding the law and enforcing Fundamental Rights’. Anyone can approach the courts if they believe that their rights have been violated. If any law passed by the Parliament violates anyone’s Fundamental Rights, the judiciary has power to declare such law null and void.
2. Re-read the list of Fundamental Rights provided in Chapter 1. How do you think the Right to Constitutional Remedies connects to the idea of judicial review?
Answer – Right to Constitutional Remedies declares that citizens can go to court for justice if they believe that any of their Fundamental Rights have been violated by the State. Hence the independence of the judiciary is necessary to uphold the rights of the citizens.
3. In the following illustration, fill in each tier with the judgments given by the various courts in the Sudha Goel case. Check your responses with others in the class.
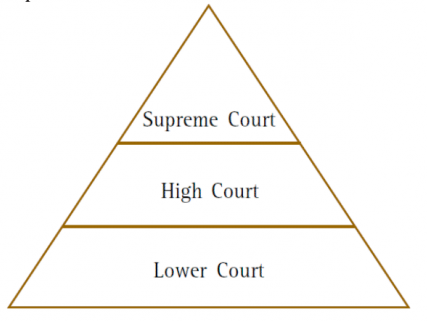
Answer – Lower Court (Trial Court): Laxman, his mother Shakuntala and his brother-in-law Subhash Chandra were sentenced to death
High Court: Laxman, Shakuntala and Subhash Chandra were acquitted.
Supreme Court: Laxman, Shakuntala were given life imprisonment while Subhash Chandra was acquitted for lack of sufficient evidence.
4. Keeping the Sudha Goel case in mind, tick the sentences that are true and correct the ones that are false.
(a) The accused took the case to the High Court because they were unhappy with the decision of the Trial Court.
(b) They went to the High Court after the Supreme Court had given its decision.
(c) If they do not like the Supreme Court verdict, the accused can go back again to the Trial Court.
Answer –
(a) The accused took the case to the High Court because they were unhappy with the decision of the Trial Court. (True)
(b) They went to the High Court after the Supreme Court had given its decision. (False)
(c) If they do not like the Supreme Court verdict, the accused can go back again to the Trial Court. (False)
5. Why do you think the introduction of Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in the 1980s is a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all?
Answer – The introduction of Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in the 1980s is a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all because it also keeps in mind the interests of the illiterate and poor who are not educated enough or cannot afford to access the Indian legal system for justice against exploitation or violation of their basic human and Fundamental Rights.
6. Re-read excerpts from the judgment on the Olga Tellis vs Bombay Municipal Corporation case. Now, write in your own words what the judges meant when they said that the Right to Livelihood was part of the Right to Life.
Answer – In the Olga Tellis vs Bombay Municipal Corporation case, the judges meant that the Right to Life had a wider meaning. It included the Right to Livelihood. Without means of livelihood, none can exist. By Livelihood one earns money to buy food, clothing, and shelter. Hence, none can be denied of his livelihood.
7. Write a story around the theme, ‘Justice delayed is justice denied’.
Answer – Students have to do this by themselves.
8. Make sentences with each of the glossary words given on the next page.
Acquit, To appeal, Compensation, Eviction, Violation.
Answer –
- Acquit: The jury decided to acquit the defendant on the grounds of lack of sufficient evidence to convict them of the crime.
- To Appeal: The defendant decided to appeal to the High Court after their lawyer said the court’s decision was not correct.
- Compensation: In compensation for the trouble caused due to flight delay, the airlines awarded the victim fifty thousand rupees.
- Eviction: The couple faced eviction because they failed to pay the monthly instalments to the bank.
- Violation: The office staff protested the company for the violation of their rights.

Leave a Reply