NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 8 Science Chapter – 7 (Conservation of Plants and Animals) has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter – 7 (Conservation of Plants and Animals)
1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called a _________.
(b) Species found only in a particular area are known as _______.
(c) Migratory birds fly to faraway places because of __________ changes.
Answer –
(a) A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called a sanctuary.
(b) Species found only in a particular area are known as endemic.
(c) Migratory birds fly to faraway places because of climatic changes.
2. Differentiate between the following.
(a) Wildlife sanctuary and biosphere reserve
Answer –
| Wildlife sanctuary | Biosphere reserve |
| Wildlife sanctuaries are the places where wild animals are protected in their natural habitats. In these areas hunting is prohibited. | Biosphere reserves are the areas tjat are used to conserve biodiversity. These areas contain many national parks and wildlife sanctuaries. |
| These areas provide protection to wild animals. | These areas help in the conservation of various types of plants, animals and microorganisms. |
| In these areas, tourism is permissible. | In these areas, no tourism is permissible. |
| Boundaries are not fixed for wildlife sanctuaries. | Boundaries are fixed for biosphere reserves. |
| Example – Chinnar Wildlife sanctuary in Kerala | Example – Pachmarhi biosphere reserve |
(b) Zoo and wildlife sanctuary
Answer –
| Zoo | Wildlife sanctuary |
| Zoo is an area where animals are kept for public exhibition. | Wildlife sanctuaries are the areas where wild animals are protected in their natural habitats. Here hunting or poaching practices are prohibited. |
| Zoos are the small areas where animals are kept inside the cages. | Wildlife sanctuaries are the large areas where animals are free to move anywhere. |
| Zoo contains the animals that are brought from the different parts of the world for exhibition. | A wildlife sanctuary contains the animals that are found locally in that area. |
| Zoos provide artificial habitats to the animals. | Animals are protected in their natural habitats. |
| Example – Delhi Zoo | Example – Sanjay Gandhi wildlife sanctuary |
(c) Endangered and extinct species
Answer –
| Endangered species | Extinct species |
| Endangered species are those species who are facing a very high risk of extinction. | Extinct species are those species which get completely extinct. |
| The members of these species are living today but their number has decreased. | There are no surviving individuals of these species. |
| We can take some measures to protect endangered species from extinction. | We can’t do anything as they are already extinct. |
| Example – African wild dog, tiger, Royal Bengal tiger, etc. | Example – Dodo, dinosaurs, etc. |
(d) Flora and fauna
Answer –
| Flora | Fauna |
| Flora refers to the plant life that can be found in a specific region. | Fauna refers to animal life that can be found in a specific region. |
| It is automatically and naturally grown greenery of a region | It includes all types of organisms from tiny bacteria to giant animals. |
| Flora can make their own food with the help of photosynthesis (the process by which plants make their own food with the help of water, carbon dioxide and sunlight). | Fauna can’t make their own food. They depend on the plants for their food. |
| Flora is studied in botany. | Fauna studied in Zoology. |
| Flora can’t move i.e. remains at one place. | Animals can move from one place to another. |
3. Discuss the effects of deforestation on the following.
(a) Wild animals
(b) Environment
(c) Villages (Rural areas)
(d) Cities (Urban areas)
(e) Earth
(f) The next generation
Answer –
(a) Wild animals – Trees are the habitats as well as sources of food for the wild animals. Deforestation leads to the destruction of the natural habitats of wild animals.
(b) Environment – Deforestation increases the temperature and pollution level of the environment. With the increase in the carbon dioxide level and a decrease in the oxygen level, it gives rise to global warming. It also lowers the level of ground water. Moreover, deforestation decreases the soil fertility and so, increases the chances of natural calamities.
(c) Villages (Rural areas) – The decline in rainfall, the decrease in soil fertility, and the chances of natural disaster affect the village life.
(d) Cities (Urban areas) – Deforestation result in global warming. It also results in the increase in the level of pollution. Hence, deforestation affects the life in cities.
(e) Earth – Deforestation decreases the fertility of soil. It changes the physical properties of soil. All these changes result in desertification.
(f) The next generation – Deforestation will majorly affect the life of next generation. The next generation will face problems at every step. Climatic conditions will be adversely affected. There will be scarcity of food and clean environment. Next generation won’t be able to see most of the animal species due to habitat loss.
4. What will happen if
(a) we go on cutting trees
Answer – Trees provide shelter to animals and birds. If trees are cut, animals and birds will lose their habitat. Trees are sources of fruits, sheds, wood. There will be a scarcity of such resources if trees are cut. Global warming will occur. Groundwater reserves also will be reduced.
(b) the habitat of an animal is disturbed
Answer – If the habitat of an animal is disturbed, the survival of animals is endangered. It will ultimately lead to its extinction.
(c) the top layer of soil is exposed
Answer – Removal of the top layer of the soil exposes the lower, hard, and rocky layers. The top layer is more fertile and contains humus. If the top layers are affected by any means, the fertility of the soil is lost and this will eventually lead to desertification.
5. Answer in brief.
(a) Why should we conserve biodiversity?
Answer – Conservation of biodiversity is essential because of the following reasons:
(i) Biodiversity maintains balance in the ecosystems.
(ii) Wild animals and plants provide a variety of commodities.
(iii) Wildlife is needed for breeding programmes in agriculture, horticulture, sericulture, apiculture, etc. Any damage to biodiversity will threaten the whole support system and will be a threat to human existence. Therefore, biodiversity needs to be conserved.
(b) Protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals. Why?
Answer – Since capturing and killing of animals by poachers is still rampant in protected forests and areas, so they are not safe for wild animals.
(c) Some tribals depend on the jungle. How?
Answer – Some tribes depend on the jungle for the fulfillment of their basic needs of life, such as food, medicine, clothing, shelter, etc.
(d) What are the causes and consequences of deforestation?
Answer – The causes of deforestation may be the following:
- Natural causes like forest fires, droughts, etc.
- Building factories and houses.
- Procuring land for cultivation.
- Making furniture and using wood as fuel.
The consequences of deforestation are:
- Natural calamities like floods, etc.
- Increase in the temperature of the earth, i.e., global warming.
- Change in the physical properties of soil.
- A decrease in groundwater level.
- Extinction of many flora and fauna.
(e) What is Red Data Book?
Answer – The Red Data Book is a sourcebook which has an international list of all plant and animal species which are endangered, that is, on the verge of extinction. The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural resources (IUCN) maintains the books and adds/removes the names of the species by conducting a comprehensive survey.
(f) What do you understand by the term migration?
Answer – Migration means the movement of a species from its own habitat to some other place during a certain period in a year for breeding or to overcome some climatic conditions.
6. In order to meet the ever-increasing demand in factories and for shelter, trees are continually being cut. Is it justified to cut trees for such projects? Discuss and prepare a brief report.
Answer – It is not justified to cut the trees at the present rate for such projects. Trees are one of the most important parts of the ecosystem. We must reduce our dependency on forest resources. It is our responsibility to protect the Earth. This can be done by proper planning for afforestation so that new trees can be planted in deforested areas.
7. How can you contribute to the maintenance of the green wealth of your locality? Make a list of actions to be taken by you.
Answer – We should take following actions for the maintenance of green wealth of our locality:
(i) We can grow more and more plants in our locality.
(ii) We can protect them and provide water to them.
(iii) All the residents should be taught about the benefits of trees.
(iv) They should also be taught about the harms of cutting of trees.
8. Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall.
Answer – Plants are the main agent to maintain the water cycle in the environment. If plants will not absorb water from soil they will not evaporate it in the environment to form clouds. If clouds will not be formed then no rainfall will take place. In this way deforestation reduces rainfall.
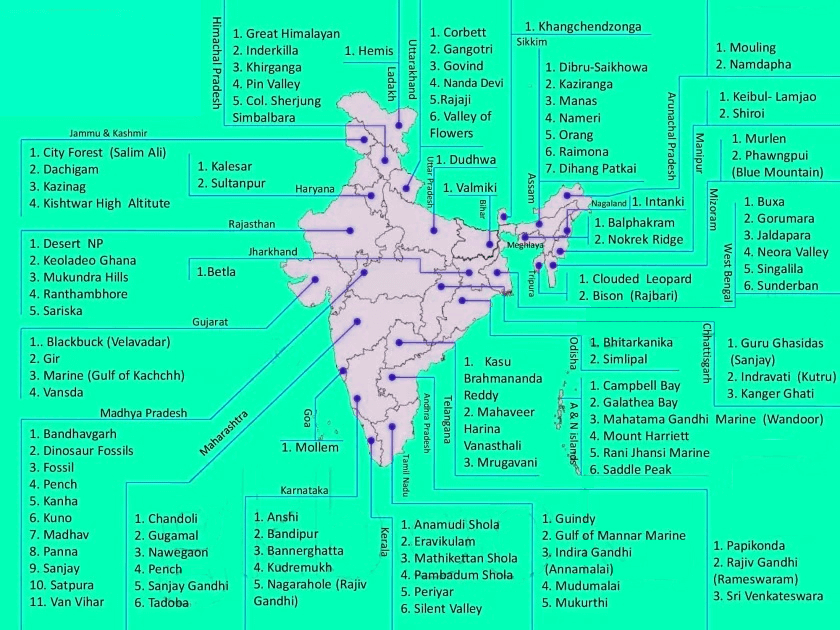
9. Find out about national parks in your state. Identify and show their location on the outline map of India.
Answer –
10. Why should the paper be saved? Prepare a list of ways by which you can save paper.
Answer – The wood pulp is used in manufacturing the papers. It takes 17 full grown trees to make one tonne of paper. So, we should save paper to protect our trees. Ways to save papers are as follows:
(i) We should save at least one sheet of paper in a day.
(ii) We should not throw paper here and there.
(iii) Waste paper should be collected and send for recycling.
(iv) We should reuse the used paper.
11. Complete the word puzzle.
Down
1. Species on the verge of extinction.
2. A book carrying information about endangered species.
5. Consequences of deforestation.
Across
1. Species which have vanished.
3. Species found only in a particular habitat.
4. Variety of plants, animals and microorganisms found in an area.
Answer –


Leave a Reply