NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 7 Science Chapter – 12 (Reproduction in Plants) has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter – 12 (Reproduction in Plants)
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called_____________.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called_____________.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as _____________.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as _____________.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of _____________, _____________ and _____________.
Answer –
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called vegetative propagation.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called unisexual flower.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as Pollination.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as fertilisation.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of wind, water and animals.
2. Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Answer – There are six types of asexual reproduction. They are:
Vegetative Propagation – In this asexual reproduction, new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds of the individual plant. Examples – Tuber of potato, the rhizome of ginger.
Budding – The bud is a small projection which gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms a new yeast cell. The new yeast cell grows, matures and produces more yeast cells. Example – Yeast.
Fragmentation – In this mode of reproduction, the growth and multiplication are done by rapidly breaking down into two or more fragments. Each fragment grows into new individuals when water and nutrients are available. Example – Algae
Spore Formation – This reproduction is done by spores which under favourable conditions germinates and develops into a new individual. Examples – Fungi like Rhizopus, Mucor, etc.
Fission – It is a type of asexual reproduction where the unicellular organism splits to form new organisms. There are two types of fission which are
- Binary fission
- Multiple fission
Examples – Unicellular organisms that undergo binary fission are amoeba, paramecium, Leishmania etc. Plasmodium undergoes the process of multiple fission.
3. Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Answer – Sexual reproduction is the process in which new organisms are created, by combining the genetic information from two individuals of different sexes. The genetic information is carried on chromosomes within the nucleus of specialized sex cells called gametes.
4. State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Answer –
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| It requires only one parents | Requires a male and female parent |
| Daughter cells formed are identical to parents and to each other. | Newly formed offsprings show variations in comparision to the parents. |
| Special reproductive organs are not required | Special reproductive organs are required |
| Ex: Yeast, rose, jasmine | Ex: Insects, animals |
5. Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Answer –
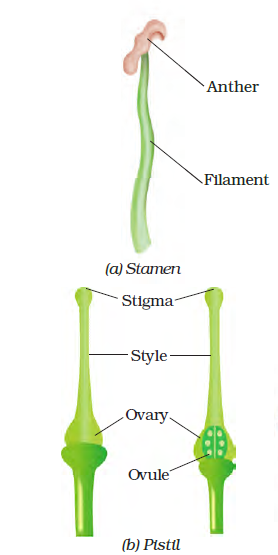
6. Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Answer –
| Self-pollination | Cross-pollination |
| In self-pollination, pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower. | In cross-pollination, pollen grains are transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same kind. |
| Self-pollination occurs only in bi-sexual flowers | It occurs in both unisexual and bisexual flowers |
7. How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
Answer – The process of fusion of male and female gametes (to form a zygote) is called fertilisation. The zygote develops into an embryo and embryo undergoes mitotic cell division to form seeds.
8. Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Answer – Seed dispersal occurs by the following agencies.
(a) Dispersal by animals – There are many ways by which birds and animals can disperse seeds. For example, birds and animals can eat the fruits and excrete the seeds away from the parent plant. Some seeds have barbs or other structures that get attached to the animal’s body and are carried to new sites. Some fruits have hooks on them which cling to fur or clothes.
(b) Dispersal by wind– Seeds that get dispersed by wind are usually smaller in size or they have wings or hair-like structures. For example, winged seeds of drumsticks, hairy fruit of sunflower, etc. are dispersed by wind.
(c) Dispersal by water — Many aquatic plants or plants that live near water has seeds that can float and are carried away by water. For example, coconuts can float and are dispersed by water.
(d) Dispersal by explosion — Sometimes the seeds are dispersed by the bursting of fruits with sudden jerks. The seeds get scattered or distributed far from the parent plant. Examples of such plants are castor and balsam.
9. Match items in Column I with those in Column II: Column I Column II
| Column – I | Column – II |
| (a) Bud | (i) Maple |
| (b) Eyes | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (c) Fragmentation | (iii) Yeast |
| (d) Wings | (iv) Bread mould |
| (e) Spores | (v) Potato |
| (vi) Rose |
Answer –
| Column – I | Column – II |
| (a) Bud | (iii) Yeast |
| (b) Eyes | (v) Potato |
| (c) Fragmentation | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (d) Wings | (i) Maple |
| (e) Spores | (iv) Bread mould |
10. Tick the correct answer:
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the
(i) leaf
(ii) stem
(iii) root
(iv) flower
Answer – (iv) flower
(b) The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called
(i) fertilisation
(ii) pollination
(iii) reproduction
(iv) seed formation
Answer – (i) fertilization
(c) Mature ovary forms the
(i) seed
(ii) stamen
(iii) pistil
(iv) fruit
Answer – (iv) fruit
(d) A spore-producing organism is
(i) rose
(ii) bread mould
(iii) potato
(iv) ginger
Answer – (ii) bread mould
(e) Bryophyllum can reproduce by its
(i) stem
(ii) leaves
(iii) roots
(iv) flower
Answer – (ii) leaves

Leave a Reply