NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 10 Science Chapter – 7 (Control and Coordination) have been provided here to help the students solve the questions from this exercise.
Chapter – 7 (Control and Coordination)
Questions
1. What is the difference between reflex action and walking ?
Answer –
| Reflex | Walking/Voluntary |
| 1. Origin. Reflex action is inborn and present in an individual right from birth. | 1. It is acquired through learning. |
| 2. Control. It is automatic. An individual cannot control it. | 2. It is under control of the will or brain. |
| 3. Intensity. It cannot be changed. | 3. It can be changed. |
| 4. Value. It has survival and protective value. | 4. It has various functions, generally other than survival and protection. |
2. What happens at the synapse between two neurons ?
Answer – At the synapse between two neurons, electric signals are converted into chemicals that can easily cross over the gap and pass on the chemical messenger to the next neuron where it is converted back to electrical signal.
3. Which part of brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body ?
Answer – Cerebellum, a part of hindbrain is responsible for maintaining posture and equilibrium of the body.
4. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick) ?
Answer – When the smell of the incense stick reaches to our nose then the olfactory receptors present in our nose detects it send this information in fore brain in the form of electrical signals. Fore brain interprets this information as the smell of incense stick where it is already stored.
5. What is the role of brain in reflex action ?
Answer – It functions as a relay centre for transferring impulse from sensory to motor neurons in several reflex actions called cerebral reflexes, e.g, closure of eyes exposed to flash of light, salivation at the sight or smell of food. In spinal reflexes it acts as information collecting and evaluation centre without any direct involvement in reflex action.
Questions
1. What are plantohormones ?
Answer – Plant hormones or phytohormones arenaturally-occurring organic substances. These are synthesized in one part of the plant body (in minute quantities) and are translocated to other parts when required. The five major types of phytohormones are auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene.
2. How is movement of leaves of Sensitive Plant different from movement of shoot towards light ?
Answer –
| Movement of leaves of a sensitive plant | Movement of a shoot towards light |
| 1. It does not depend on the direction of stimulus applied. | 1. Depends on the direction of stimulus applied. |
| 2. Nastic movement | 2. Tropic movement |
| 3. Touch is the stimulus | 3. Light is the stimulus |
| 4. Caused by the sudden loss of water from the swellings at the base of leaves | 4. Caused by the unequal growth on the two sides of the shoot. |
| 5. Not a growth movement | 5. Growth movement |
| 6. Occurs very fast | 6. Occurs slowly |
3. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth ?
Answer – Auxin is an example of growth-promoting plant hormone.
4. How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support ?
Answer – Auxin is synthesized at the shoot tip. It helps the cell grow longer. When a tendril comes in contact with a support, auxin stimulates faster growth of the cells on the opposite side, so that the tendril forms a coil around the support. This makes the tendrils appear as a watch spring.
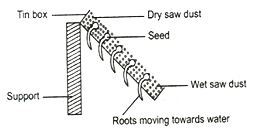
5. Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer – Take a tin box with hole at bottom. Fill it with moist saw dust. Sow some gram seeds in it. Keep the tin box in tilted position. When seeds start germinating, water the saw dust only in lower side of the tin box. You will observe that the radicle move towards the wet saw dust. This shows that root is positively hydrotropic.
Questions
1. How does chemical coordination take place in animals ?
Answer – The chemical coordination is maintained by hormones. These are secreted by endocrine glands. These hormones are poured into blood through which they reach the target tissue or organ to act.
2. Why is the use of iodised salt advisable ?
Answer – Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make thyroxin hormone. In case, iodine is absent in our diet, there is a possibility of Goitre. Iodised common salt contains proper content of iodine. To avoid deficiency of iodine, iodised salt is recommended.
3. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into blood ?
Answer – Adrenaline/emergency hormone/triple F hormone
- Reduces blood supply to peripheral blood vessels and gastrointestinal tract,
- More blood flows to skeletal and heart muscles.
- Increases breathing and gives more oxygen to muscles,
- Increases heart rate,
- Mobilises more glucose to muscles for higher activity.
4. Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin ?
Answer – Diabetes is caused due to non or less secretion of hormone insulin by pancreas. In such person, the blood sugar level is high. Insulin converts extra sugar present in blood into glycogen. Patients suffering from diabetes are given insulin injection to control their blood sugar level.
Exercises
1. Which of the following is a plant hormone ?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxine
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin.
Answer – (d) Cytokinin
2. The gap between two neurons is called
(a) Dendrite
(b) Synapse
(c) Axon
(d) Impulse.
Answer – (b) Synapse
3. The brain is responsible for
(a) Thinking
(b) Regulating the heart beat
(c) Balancing
(d) All the above.
Answer – (d) All the above
4. What is the function of receptors in our body ? Think of situation where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise ?
Answer – Receptors detect all the information from our environment. These receptors are located in our sense organs. In case any of the receptors do not work properly we will not be able to perceive that particular information.
5. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its functions.
Answer – Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system. The three main parts of a neuron are axon, dendrite, and cell body.
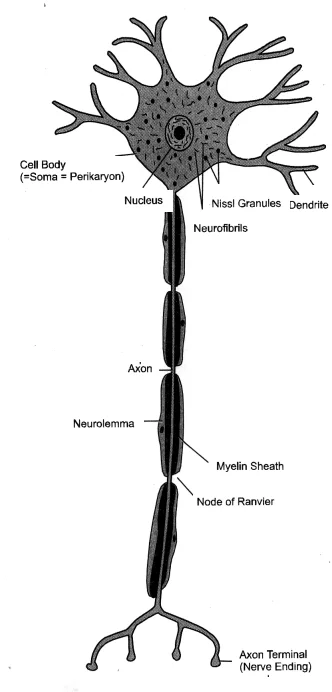
Functions of the three parts of a neuron:
Axon – It conducts messages away from the cell body.
Dendrite – It receives information from axon of another cell and conducts the messages towards the cell body.
Cell body – It contains nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles. It is mainly concerned with the maintenance and growth.
6. How does phototropism occur in plants ?
Answer – Movement of shoot towards light is called phototropism. This movement is caused due to more growth of cells towards the shaded side of the shoot as compared to the side of shoot towards light. More growth of cells is due to secretion of auxin towards the shaded side.
7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of spinal cord injury ?
Answer – In case of a spinal cord injury, signals coming from the nerves, as well as the signals coming to the receptors, will be disrupted. Both these signals meet in a bundle in the spinal cord. Hence, both these signals get disrupted.
8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants ?
Answer –
- Plants do not have nervous systems or muscles for movement.
- But they have hormones for chemical coordination.
- Hormones are chemical messengers that respond to internal and external stimuli.
- They are produced in small quantities in a part of the plant and then transported through xylem, phloem or by diffusion to other parts.
- They may promote or inhibit growth
For example let us consider sunflowers growing towards the sunlight.
- Once the plant detects sunlight , the hormone auxin is secreted at the shoot tips .
- The secreted auxins diffuse towards the shady side of the plant
- This makes the cells on the shady side grow longer
- Thus, the plant appears to bend towards light .
9. What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism ?
Answer – An organism needs control and coordination system for the following functions :
(i) To save the body of the organisms from the harmful changes in the environment.
(ii) To control the speed of voluntary and involuntary actions.
(iii) To have the capability to think and learn for responding to any stimuli.
10. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other ?
Answer –
| Involuntary actions | Reflex actions |
| 1. Those actions which occur immediately without any thinking are called involuntary actions. | 1. Reflex action is an immediate response to an event which does not require any processing by brain. |
| 2. Involuntary actions are controlled by mid and hind brain. Example: Breathing, beating of heart, etc. |
2. Reflex actions are controlled by spinal cord. Example: Sneezing, coughing, etc. |
11. Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Answer –
| Nervous mechanism | Hormonal mechanism |
| It is a fast process. | It is a slow process. |
| Arteries and glands are affected. | It affects the target organ. |
| It transmits in electrochemical form. | It transmits in chemical form. |
| It does not control metabolism. | It controls metabolism. |
| Growth is not affected. | Growth is affected. |
12. What is the difference between the manner in which movement in Sensitive Plant and movement in our legs takes places ?
Answer –
| Movement in a sensitive (mimosa) plant | Movement in legs of a human |
| 1. The leaves of a sensitive plant like mimosa are sensitive to touch. | 1. Leg is in control of nerve muscles. |
| 2. It is not controlled by any part of the plant. | 2. It is controlled by brain and spinal cord. |
| 3. In this, cells change their shape on changing the amount of water in them | 3. Amount of water has no effect on the movement of muscles. |
| 4. The movement in a sensitive plant are nastic movement. | 4. The movement in our leg is due to voluntary nervous system. |

Leave a Reply