NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 10 Science Chapter – 4 (Carbon and Its Compounds) has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter – 4 (Carbon and Its Compounds)
Questions
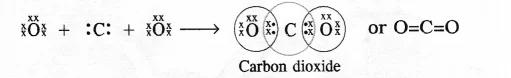
1. What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2 ?
Answer – Electron dot structure of CO2 is
2. What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur ?
Answer – Electron dot structure of a sulphur molecule

Questions
1. How many structural isomers you can you draw for pentane ?
Answer – Three structural isomers are possible for pentane :
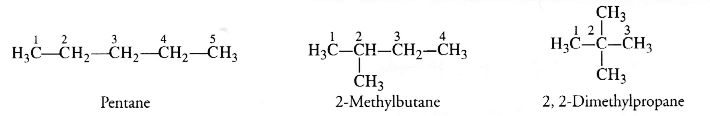
2. What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us ?
Answer – Two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us are as given below:
- Carbon has six valence electrons which is actually a high number of valency.
- Covalent bonding happens easily with carbon atoms and numerous others, such as oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen, sulphur, hydrogen, etc.
3. What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane ? (CBSE 2013)
Answer – Cyclopentane is a cyclic compound with formula C5H12 The structure of the compound may be represented as :

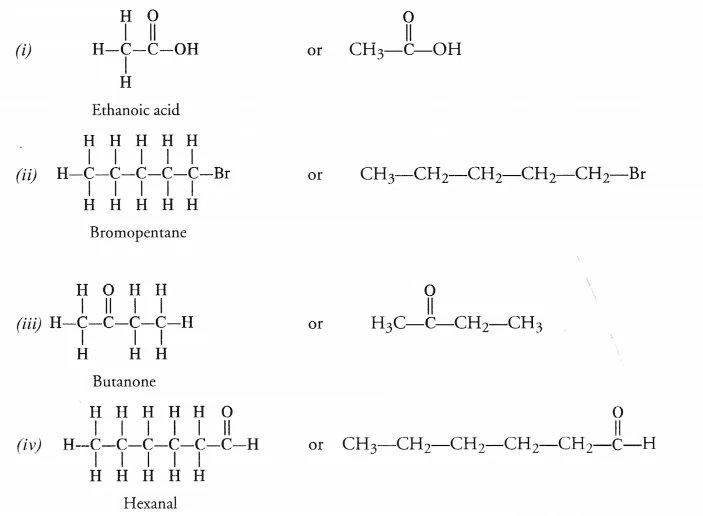
4. Draw the structures of the following compounds :
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Bromopentane
(iii) Butanone
* Are structural isomers possible for bromopentane ?
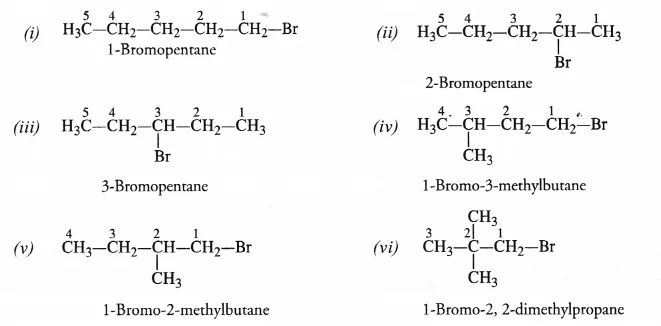
Answer –
Bromopentane has a chain of five carbon atoms. It can exist in a number of forms which are structural isomers.
5. How would you name the following compounds ?
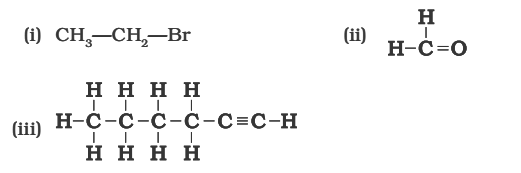
Answer –
(i) Bromoethane
(ii) Hex-l-yne
(iii) Methanal
Questions
1. Why is the conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction ?
Answer – Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) has one oxygen atom more and two hydrogen atoms less than ethanol (C2H5OH). In general,
- Loss of hydrogen is known as oxidation.
- Gain of oxygen is known as oxidation.
Therefore, it is an oxidation reaction.
2. A mixture of ethyne and oxygen is used for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used ?
Answer – When ethyne is burnt in oxygen, large quantity of heat alongwith light is produced. The heat evolved can be used for gas welding which is usually carried to weld small broken pieces of articles made up of iron.
![]()
Air mainly contains a mixture of nitrogen (4 parts) and oxygen (1 part). As we know, nitrogen gas does not support combustion. This means that in air, only oxygen will help in the combustion of ethyne. Therefore, it is always better to use oxygen for the combustion of ethyne.
Questions
1. How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid ?
Answer – In reaction with sodium carbonate, carboxylic acids produce carbon dioxide gas which turns lime water milky, whereas alcohols do not give this reaction. This experiment can be used to distinguish alcohol and carboxylic acid.
The reaction of the carboxylic acid with sodium carbonate:
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
2. What are oxidising agents ?
Answer – Oxidising agents are those compounds which either remove hydrogen or add oxygen to a compound. For example, halogens, potassium nitrate, and nitric acid.
Questions
1. Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent ?
Answer – No, it is not possible. Actually detergents produce foam in any type of water ; whether hard or soft.
Therefore, a distinction between the two cannot be made. However, soaps can be used for this purpose.
2. People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding soap, they beat the clothes on a stone or beat them with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine Why is this agitation necessary to get clean clothes ?
Answer – The purpose of soap or detergent in washing is to reduce friction between oil drops carrying dirt particles and water so that they may mix with each other. All the methods that have been suggested loosen the bonds between the dust or oil particles and fabrics of clothes. The agitation helps in washing the clothes.
Exercise
1. Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has :
(a) G covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds
Answer – (b) 7 covalent bonds
2. Butanone is a four carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol.
Answer – (c) ketone
3. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely
(b) the fuel is not burning completely
(c) the fuel is wet
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer – (b) the fuel is not burning completely
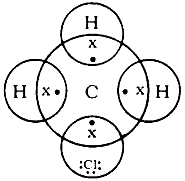
4. Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer – Covalent bond is formed by sharing of electrons between two atoms. It is non-ionic in nature.
5. Draw the electron dot structures for
(i) ethanoic acid
(ii) H2S
(iii) propanone
(iv) F2.
Answer:
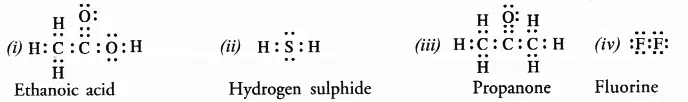
6. What is homologous series ? Explain with an example.
Answer – A homologous series is a series of carbon compounds that have different numbers of carbon atoms but contain the same functional group.
For example, methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc. are all part of the alkane homologous series. The general formula of this series is CnH2n+2.
Methane CH4
Ethane CH3CH3
Propane CH3CH2CH3
Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3
It can be noticed that there is a difference of −CH2 unit between each successive compound.
7. How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties ?
Answer –
| Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| It does not react with sodium hydrogen carbonate | Bubbles and fizzes with sodium hydrogen carbonate |
| A good smell | Smells like vinegar |
| No action in litmus paper | Blue litmus paper to red |
| Burning taste | Sour taste |
8. Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water ? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also ?
Answer – Soap is sodium or potassium salt of long chain fatty acid. Two ends of soap molecules have different properties. The ionic end is hydrophilic. It dissolve in water while the hydrogen chain is hydrophobic, it dissolve in hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbon chains are oriented towards the oil droplet while the ionic ends are oriented towards water. Micelles formation will not take place in ethanol.
9. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels in most applications?
Answer – Carbon on combustion gives carbon dioxide and water. This reaction is accompanied by evolution of heat and light. The same is true for compounds of carbon. That is why carbon and its compounds are used as fuel for most applications.
10. Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer – Hard water contains hydrogen carbonates, chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium which reacts with soap to form scum. For example, calcium chloride reacts with soap to form scum.
Sodium stearate + Calcium chloride à sodium chloride + Calcium stearate(scum)
11. What change will you observe by testing soap with litmus paper (blue or red) ?
Answer – Soap is sodium or potassium salt of fatty acid. It is obtained by treating of oil with caustic soda. Sodium stearate is thus a salt of weak acid and strong base. Its water solution will be slightly alkaline and will turn red litmus red.
12. What is hydrogenation ? What is its industrial application ?
Answer – Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in presence of catalysts such as palladium or nickel to give saturated hydrocarbons. This process is called hydrogenation.
It is commercially used for converting vegetable oils to ‘vanaspati’ ghee in presence of nickel as catalyst.
13. Which of the listed hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions :
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4 ?
Answer – C3H6 and C2H2 will undergo addition reactions.
14. Give a test that can be used to differentiate between butter and cooking oil.
Answer – Butter and cooking oil can be differentiated with the help of bromine water test. Cooking oil will decolorize the red colour of bromine water on shaking while butter will not.
15. Explain the mechanism of cleansing action of soap.
Answer – Soap are sodium or potassium salt of fatty acids. Two ends of molecules of soap behave differently. This ionic end is hydrophilic and it is oriented towards water. The other hydrocarbon end is hydrophobic and it is oriented towards dirt which is oily in nature. A micelle formation around the oily dirt takes place. When flushed with excess of water, the micelle containing the dirt is removed, thus cleaning the clothes, etc.

Leave a Reply