NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 10 Science Chapter – 12 (Electricity) has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter – 12 (Electricity)
Questions
1. What does an electric circuit mean ?
Answer – An electric circuit consists of electric devices, switching devices, source of electricity, etc. that are connected by conducting wires.
2. Define the unit of current.
Answer – Unit of electric current is ampere. Electric current in a conductor is said to be 1 A if 1 coulomb charge flows through the cross-section of the conductor in 1 second.
3. Calculate the number of electrons consisting one coulomb of charge.
Answer – Charge on one electron = 1.6 x 10-19 coulomb.
No of electron in one coulomb of charge = 1/1.6 x 10-19
= 6.25 x 1018
Questions
1. Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor. (CBSE 2008)
Answer – A cell or battery.
2. What is meant by saying that a potential difference between two points is 1 V ?
Answer – Potential difference between two points is 1 V if 1 joule work is done in moving 1 coulomb charge from one point to another point.
3. How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery ?
Answer – Energy = Charge × Potential difference
= 1 C × 6 V = 6 J.
Questions
1. On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend ?
Answer – The resistance of a conductor depends upon the following factors:
- Length of the conductor.
- Cross-sectional area of the conductor.
- Material of the conductor
- Temperature of the conducto
2. Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source Why ?
Answer – The current flows more easily through a thick wire as compared to thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source. It is due to the reason that resistance increases with decrease in thickness.
3. Let the resistance of an electric component remains constant while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it?
Answer – It is given that resistance R of the electrical component remains constant but the potential difference across the ends of the component decreases to half of its value.
Hence, as per Ohm’s law, new current also decreases to half of its original value.
4. Why are coil of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal ?
Answer – The resistivity of an alloy is higher than the pure metal. Moreover, at high temperatures, the alloys do not melt readily. Hence, the coils of heating appliances such as electric toasters and electric irons are made of an alloy rather than a pure metal.
5. Use the data in Table 12.2 to answer the following:
(a) Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor?
(b) Which material is the best conductor?
Answer – Table 12.2 Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C
| − | Material | Resistivity (Ω m) |
| Conductors |
Silver | 1.60 × 10−8 |
| Copper | 1.62 × 10−8 | |
| Aluminium | 2.63 × 10−8 | |
| Tungsten | 5.20 × 10−8 | |
| Nickel | 6.84 × 10−8 | |
| Iron | 10.0 × 10−8 | |
| Chromium | 12.9 × 10−8 | |
| Mercury | 94.0 × 10−8 | |
| Manganese | 1.84 × 10−6 | |
| Alloys |
Constantan (alloy of Cu and Ni) | 49 × 10−6 |
| Manganin (alloy of Cu, Mn and Ni) | 44 × 10−6 | |
| Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe) | 100 × 10−6 | |
| Insulators |
Glass | 1010 − 1014 |
| Hard rubber | 1013 − 1016 | |
| Ebonite | 1015 − 1017 | |
| Diamond | 1012 − 1013 | |
| Paper (dry) | 1012 |
(a) Resistivity of iron = 10.0×10−8Ωm
Resistivity of mercury =94.0×10−8 Ωm.
Resistivity of mercury is more than that of iron. This implies that iron is a better conductor than mercury.
(b) It can be observed from Table 12.2 that the resistivity of silver is the lowest among the listed materials. Hence, it is the best conductor.
Questions
1. Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a batteries of three of 2 V each, a 5 Ω resistor, 8 Ω resistor and a 12 Ω resistor and a plug key, all connected in series.
Answer – The schematic diagram of circuit is as follows:
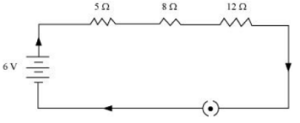
2. Redraw the circuit of question 12, putting an ammeter to measure the current through the resistor and a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across 12 Ω resistor. What would be the reading in the ammeter ?
Answer – Here ammeter A has been joined in series of circuit and voltmeter V is joined in parallel to 12 ohms’ resistor.
Total voltage of battery V = 3×2 = 6 V.
Total resistance R = R1+ R2+ R3 = 5 Ω + 8 Ω + 12 Ω = 25 Ω
Ammeter reading (current) = I = V/R = 6/25 = 0.24 A.
Voltmeter reading = IR = 0.24 × 12 = 2.88 V.
Questions
1. Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel :
(a) 1 Ω and 106 Ω
(b) 1 Ω and 103 Ω and 106 Ω.
Answer – When the resistances are joined in parallel, the resultant resistance in parallel arrangement is given by:
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
(a) 1/R = 1/1+ 1/106 = 1+ 10-6
R = 1 Ω
(b) 1/R = 1/1 + 1/103 + 1/106 = 1 + 10-3 + 10-6
R = 1 Ω
2. An electric lamp of 100 W, a toaster of resistance 50 Ω, and a water filter of resistance 500 Ω are connected in parallel to 220 V source. What is the resistance of an electric iron connected to the same source that takes as much current as all three appliances and what is the current through it ?
Answer – Here, voltage (V) = 220 V
R1 = 100 Ω,
R2 = 50 Ω
R3 = 500 Ω
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
1/R = 1/100+1/50 +1/500 = 16/500
R = 500/16 = 31.25 Ω
The resistance of electric iron, which draws as much current as all three appliances take together = R = 31.25 Ω.
Current passing through electric iron (I) = V/R = 220/31.25 = 7.04 A.
3. What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series?
Answer – Advantage of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery are as follows:
(i) Voltage across each connecting electrical device is same and device take current as per its resistance.
(ii) Separate on/off switches can be applied across each device.
(iii) Total resistance in parallel circuit decreases, hence, a great current may be drawn from cell.
(iv) If one electrical device is damaged; then other devices continue to work properly.
4. How can three resistors of resistance 2 Ω, 3 Ω and 6 Ω be connected to give a total resistance of
(a) 4 Ω
(b) 1 Ω?
Answer – There are three resistors of resistances 2 Ω, 3 Ω, and 6 Ω respectively.
(a) The following circuit diagram shows the connection of the three resistors.
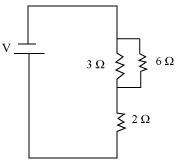
Here, 6 Ω and 3 Ω resistors are connected in parallel.
Therefore, their equivalent resistance will be given by
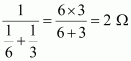
This equivalent resistor of resistance 2 Ω is connected to a 2 Ω resistor in series.
Therefore, equivalent resistance of the circuit = 2 Ω + 2 Ω = 4 Ω
Hence, the total resistance of the circuit is 4 Ω.
(b) The following circuit diagram shows the connection of the three resistors.
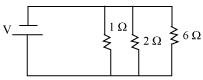
All the resistors are connected in series. Therefore, their equivalent resistance will be given as.
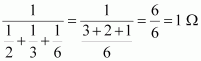
Therefore, the total resistance of the circuit is 1 Ω.
5. What is (a) the highest, (b) the lowest total resistance that can be secured by combinations of four coils of resistance 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω, 24 Ω?
Answer – There are four coils of resistances 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω and 24 Ω respectively.
(a) If these coils are connected in series, then the equivalent resistance will be the highest, given by the sum 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω + 24 Ω = 48 Ω
(b) If these coils are connected in parallel, then the equivalent resistance will be the lowest, given by
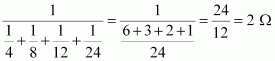
Therefore, 2 Ω is the lowest total resistance.
Questions
1. Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
Answer – The heating element of an electric heater is a resistor. The amount of heat produced by it is proportional to its resistance. The resistance of the element of an electric heater is very high. As current flows through the heating element, it becomes too hot and glows red. On the other hand, the resistance of the cord is low. It does not become red when current flows through it.
2. Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulomb of charge in one hour through a potential difference of 50 V.
Answer –
Charge transferred (Q) = 96000 C, time = 1 hour = 60 x 60 = 3600 s and potential difference (V) = 50 V.
Heat generated (H) = VIt = V.Q = 50 x 96000 = 4800000 j = 4.8 x 106 j.
3. An electric iron of resistance 20 takes a current of 5 A. Calculate the heat developed in 30 s.
Answer – Resistance of electric iron (R) = 20 Ω, current (I) = 5 A and time = 30 s.
Heat generated (H) = I2Rt = 52 x 20 x 30 = 15000 j.
Questions
1. What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current?
Answer – Electric power determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current.
2. An electric motor takes 5 A from a 220 V line. Determine the power of the motor and energy consumed in 2 h.
Answer –
It is given that current drawn by electric motor (I) = 5 A. the line voltage V = 220 V time (t) = 2 h.
Power of motor (P) = P = VI = 220 × 5 = 1100 W and the energy consumed (E) = Pt
1100 W × 2 h = 2200 Wh or 2.2 kWh.
Exercise
1. A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this combination is R’, then the ratio R/R’ is
(a) 1/25
(b) 1/5
(c) 5
(d) 25
Answer – (d) 25
Resistance of each part = R/5
All the five parts are connected in parallel. Hence, equivalent resistance (R’) is given as
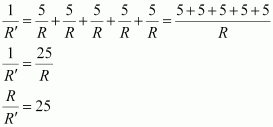
2. Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit ?
(a) I2R
(b) IR2
(c) VI
(d) V2/R
Answer – (b) IR2
Electrical power is given by the expression P = VI ———- (i)
According to Ohm’S law, V = IR —————- (ii)
Where, V = Potential difference, I = Current, R = Resistance
P = VI
From equation (i), it can be written
P = (IR) × I
P = I2R
From equation (ii), it can be written
I = V/R
P = V × V/R
P = V2/R
P = VI = I2R = V2/R
Power P cannot be expressed as IR2.
3. An electric bulb is rated as 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V the power consumed will be
(a) 100 W
(b) 75 W
(c) 50 W
(d) 25 W
Answer – (d) 25 W
P = VI = V2/R
R = V2/P
Power rating, P = 100 W
Voltage, V = 220 V
Resistance, R = 2202/100 = 484 Ω
The resistance of the bulb remains constant if the supply voltage is reduced to 110 V. If the bulb is operated on 110 V, then the energy consumed by it is given by the expression for power as
∴ P’ = V’2/R
P’ = 1102/484 = 25 W
Therefore, the power consumed will be 25 W.
4. Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then parallel in an electric circuit. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 1
(c) 1 : 4
(d) 4 : 1
Answer – (c) 1 : 4
5. How is voltmeter connected in circuit to measure the potential difference between two points ?
Answer – To measure the potential difference between two points, a voltmeter should be connected in parallel to the points.
6. A copper wire has diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity of 1.6 x 10-8 Ω m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance 10 Ω ? How much does the resistance change if diameter is doubled ?
Answer – Diameter of wire (d) = 0.5 mm,
Resistivity (ρ) 1.6 x 10-8 Ωm,
Resistance (R) = 10 Ω.
R = ρL/A
L = πD2R/4ρ
= 22 × (5 × 10-4) 2 / 7 × 4 × 1.6 ×10-8
= 122.5 m
If the diameter is doubled for given length of given material resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-section area of wire.
7. The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference V across the resistor are given below :
| I (amperes ) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| V (volts) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of that resistor.
Answer –
The plot between voltage and current is called IV characteristic. The voltage is plotted on x-axis and current is plotted on y-axis. The values of the current for different values of the voltage are shown in the given table.
| V (volts) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
| I (amperes) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
The IV characteristic of the given resistor is plotted in the following figure.
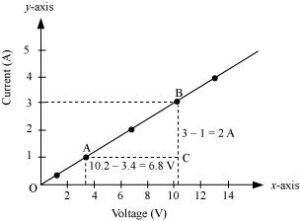
The slope of the line gives the value of Resistance(R) as,
Slope = 1/R = BC/AC = 2/6.8
R = 6.8/2 = 3.4 Ω
Therefore,the resistance of register is 3.4Ω.
8. When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistance, there is a current of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Find the value of resistance of the resistor.
Answer – Voltage of battery = V = 12 V,
Current (I) = 2.5 mA = 2.5 × 10-3 A
Resistance (R) = V/I = 12V/ 2.5 × 10-3 A
= 4800 Ω.
9. A battery of 9 V is connected in series with resistors of 0.2 Ω, 0.3 Ω, 0.4 Ω, 0.5 Ω and 12 Ω respectively. How much current would flow through 12 Ω resistor ?
Answer – Potential difference (V) = 9 V.
Total resistance (R) = R1+ R2+ R3+R4 +R5
= 0.2 +0.3 + 0.5 + 0.5 + 12 = 13.4 Ω
Current in the circuit (I) = V/R = 9 V / 13. 4 Ω = 0.67 A.
In series circuit same current flows through all the resistance, hence current of 0.67 A will flow through 12 Ω resistor.
10. How many 176 Ω resistors (in parallel) are required to carry 5 A on 220 V line ?
Answer – Let a resistor of 176 Ω are joined in parallel. Then their combined resistance (R)
1/R = 1/176 + 1/176 …… times = n/176 or R = 176/n Ω
It is given that V= 220 V and I = 5 A
R = V/I or 176/n = 220/5 = 44 Ω
n = 176/44 = 4
4 resistors should be joined in parallel.
11. Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance 6 Ω so that the combination has resistance of (i) 9 Ω (ii) 4 Ω.
Answer – It is given here that R1 = R2 = 6 Ω.
(i) To get net resistance of 9 Ω we should join three resistors as below:

(ii) To get 4 Ω net resistance we should join three resistors as below:

12. Several electric bulbs designed to be used on a 220 V electric supply line, are rated 10 W. How many lamps can be connected in parallel with each other across the two wires of 220 V line if the maximum allowable current is 5 A?
Answer – Each bulb is rated as 10 W, 220 V,
It draws a current (I) = P/V = 10 W/220
V = 1/22 A.
As the maximum allowable current is 5 A and all lamps are connected in parallel, hence maximum number of bulbs joined in parallel with each other = 5 × 22 = 110.
13. A hot plate of an electric oven connected to a 220 V line has two resistance coils A and B. Each of 24 Ω resistances, which may be used separately, in series or in parallel. What are the currents in the three cases?
Answer – It is given that potential difference (V) = 220 V.
Resistance of coil (A) = Resistance of coil (B) = 24 Ω
(i) When either coil is used separately, the circuit (I) = V/R = 220 V/ 24 Ω = 9.2 A.
(ii) When two coils are used in series total resistance (R) = R1 + R2 = 24 +24 = 48 Ω
Current flowing (I) = V/ R = 220 V/ 48 Ω = 4.6 A.
(iii) When two coils are joined in parallel. Total resistance (R) = 1/24 + 1/24
= 2/24, R = 12 Ω.
Current (I) = V/R = 220 V / 12 Ω = 18.3 A.
14. Compare the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits:
(i) a 6-volt battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors and,
(ii) a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω and Ω resistors.
Answer –
(i) When a 2 Ω resistor is joined t a 6 V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors. Total resistance (R) = 2 + 1 + 2 = 5 Ω.
Current (I) = 6 V/5 Ω = 1.2 A
Power used in 2 A resistor = I2R = 2.88 W
(ii) When 2 Ω resistor is joined to a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω resistor and 2 Ω resistors, the current flowing in 2 Ω = 4 V/ 2 Ω = 2 A/.
Power used in 2 Ω resistor = I2R = 8 W
Ratio = 2.88/8 = 0.36 : 1
15. Two lamps, one rated 100 W at 220 V, and the other 60 W at 220 V are connected in parallel to electric mains supply. What current is drawn from the line if the supply voltage is 220 V?
Answer –
Current drawn by 1st lamp rated 100 W at 220 V = P/V = 100/ 220 = 5/11 A.
Current drawn by 2nd lamp rated 60 W at 220 V = 60/220 = 3/11 A.
In parallel arrangement the total current = I1 +I2 = 3/11+ 5/11 = 8/11 = 0.73 A.
16. Which uses more energy, a 250 W TV set in 1 hour, or a 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes?
Answer –
Energy used by a TV set of power 250 W in 1 hour = P x t = 250 Wh.
Energy used by toaster of power 1200 W in 10 minute (10/60 h)
= P x t = 1200 W x 10/60 h = 200 Wh.
17. An electric heater of resistance 8 draws 15 A from the service mains for 2 hours. Calculate the rate at which heat is developed in the heater.
Answer –
Resistance of electric heater (R) = 8 Ω, current (I) = 15 A.
Rate at which heat developed in the heater = I2Rt/t = 15 x 15 x 8 = 1800 W.
18. Explain the following:
(a) Why is the tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps?
Answer – For filament of electric lamp we require a strong metal with high melting point. Tungsten is used exclusively for filament of electric lamps because its melting point is extremely high.
(b) Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
Answer – Conductors of electric heating devices are made of an alloy rather than a pure metal due to high resistivity than pure metal and high melting point to avoid getting oxidized at high temperature.
(c) Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits?
Answer – Series arrangement is not used for domestic circuits as current to all appliances remain same in spite of different resistance and every appliance cannot be switched on/ off independently.
(d) How does the resistance of wire vary with its area of cross-section?
Answer – Resistance of a wire is inversely proportional to its cross-section area.
(e) Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electric transmission?
Answer – Copper and aluminium wires are usually employed for electricity transmission because they are good conductor with low resistivity. They are ductile also to be drawn into thin wires.

Leave a Reply