NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
Chapter – 4 (Quadratic Equations)
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter – 4 Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.4 has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter : 4 Quadratic Equations
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 4.1
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 4.2
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 4.3
Exercise – 4.4
1. Find the nature of the roots of the following quadratic equations. If the real roots exist, find them:
(i) 2x2 – 3x + 5 = 0
(ii) 3x2 – 4√3x + 4 = 0
(iii) 2x2 – 6x + 3 = 0
Solutions –
(i) 2x2 – 3x + 5 = 0
Comparing the equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 2, b = -3 and c = 5
We know, discriminant = b2 – 4ac
⇒ ( – 3)2 – 4 (2) (5)
⇒ 9 – 40
⇒ – 31
As you can see, b2 – 4ac < 0
Therefore, no real root is possible for the given equation, 2x2 – 3x + 5 = 0.
(ii) 3x2 – 4√3x + 4 = 0
Comparing the equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 3, b = -4√3 and c = 4
We know, Discriminant = b2 – 4ac
⇒ (-4√3)2 – 4(3)(4)
⇒ 48 – 48 = 0
As b2 – 4ac = 0,
Real roots exist for the given equation, and they are equal to each other.
Hence, the roots will be –b/2a and –b/2a.
–b/2a = -(-4√3)/2×3 = 4√3/6 = 2√3/3 = 2/√3
Therefore, the roots are 2/√3 and 2/√3.
(iii) 2x2 – 6x + 3 = 0
Comparing the equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 2, b = -6, c = 3
As we know, discriminant = b2 – 4ac
⇒ (-6)2 – 4 (2) (3)
⇒ 36 – 24
= 12
As b2 – 4ac > 0,
Therefore, there are distinct real roots that exist for this equation, 2x2 – 6x + 3 = 0.
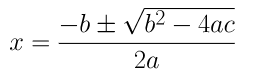
⇒ (-(-6) ± √(-62 – 4(2)(3)))/ 2(2)
⇒ (6±2√3 )/4
⇒ (3±√3)/2
Therefore, the roots for the given equation are (3+√3)/2 and (3-√3)/2.
2. Find the values of k for each of the following quadratic equations so that they have two equal roots.
(i) 2x2 + kx + 3 = 0
(ii) kx (x – 2) + 6 = 0
Solutions –
(i) 2x2 + kx + 3 = 0
Comparing the given equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 2, b = k and c = 3
As we know, discriminant = b2 – 4ac
⇒ (k)2 – 4(2) (3)
⇒ k2 – 24
For equal roots, we know,
Discriminant = 0
⇒ k2 – 24 = 0
⇒ k2 = 24
⇒ k = ±√24 = ±2√6
(ii) kx(x – 2) + 6 = 0
kx2 – 2kx + 6 = 0
Comparing the given equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = k, b = – 2k and c = 6
We know, Discriminant = b2 – 4ac
⇒ (– 2k)2 – 4 (k) (6)
⇒ 4k2 – 24k
For equal roots, we know,
⇒ b2 – 4ac = 0
⇒ 4k2 – 24k = 0
⇒ 4k (k – 6) = 0
Either 4k = 0 or k = 6 = 0
⇒ k = 0 or k = 6
However, if k = 0, then the equation will not have the terms ‘x2‘ and ‘x‘.
Therefore, if this equation has two equal roots, k should be 6 only.
3. Is it possible to design a rectangular mango grove whose length is twice its breadth and the area is 800 m2? If so, find its length and breadth.
Solution – Let the breadth of the mango grove be l.
The length of the mango grove will be 2l.
Area of the mango grove = (2l) (l)= 2l2
⇒ 2l2 = 800
⇒ l2 = 800/2
⇒ l2 = 400
⇒ l2 – 400 =0
Comparing the given equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 1, b = 0, c = 400
As we know, discriminant = b2 – 4ac
⇒ (0)2 – 4 × (1) × ( – 400) = 1600
Here, b2 – 4ac > 0
Thus, the equation will have real roots. And hence, the desired rectangular mango grove can be designed.
⇒ l = ±20
As we know, the value of length cannot be negative.
Therefore, the breadth of the mango grove = 20 m.
Length of the mango grove = 2 × 20 = 40 m.
4. Is the following situation possible? If so, determine their present ages. The sum of the ages of the two friends is 20 years. Four years ago, the product of their age in years was 48.
Solution – Let’s say the age of one friend is x years.
Then, the age of the other friend will be (20 – x) years.
Four years ago,
Age of first friend = (x – 4) years
Age of second friend = (20 – x – 4) = (16 – x) years
As per the given question, we can write,
⇒ (x – 4) (16 – x) = 48
⇒ 16x – x2 – 64 + 4x = 48
⇒ – x2 + 20x – 112 = 0
⇒ x2 – 20x + 112 = 0
Comparing the equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 1, b = -20 and c = 112
Discriminant = b2 – 4ac
= (-20)2 – 4 × 112
= 400 – 448 = -48
⇒ b2 – 4ac < 0
Therefore, there will be no real solution possible for the equations. Hence, the condition doesn’t exist.
5. Is it possible to design a rectangular park with a perimeter of 80 and an area of 400 m2? If so, find its length and breadth.
Solution – Let the length and breadth of the park be l and b.
Perimeter of the rectangular park = 2 (l + b) = 80
So, l + b = 40
Or, b = 40 – l
Area of the rectangular park = l×b = l(40 – l) = 40l – l2 = 400
l2 – 40l + 400 = 0, which is a quadratic equation.
Comparing the equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 1, b = -40, c = 400
Since discriminant = b2 – 4ac
⇒ (-40)2 – 4 × 400
⇒ 1600 – 1600 = 0
Thus, b2 – 4ac = 0
Therefore, this equation has equal real roots. Hence, the situation is possible.
The root of the equation,
l = –b/2a
l = -(-40)/2(1) = 40/2 = 20
Therefore, the length of the rectangular park, l = 20 m
And the breadth of the park, b = 40 – l = 40 – 20 = 20 m.

Leave a Reply