NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
Chapter – 3 (Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables)
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter – 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.7 has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter : 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 3.1
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 3.2
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 3.3
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 3.4
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 3.5
- NCERT Class 10 Maths Solution Ex – 3.6
Exercise – 3.7
1. The ages of two friends Ani and Biju differ by 3 years. Ani’s father Dharam is twice as old as Ani and Biju is twice as old as his sister Cathy. The ages of Cathy and Dharam differ by 30 years. Find the ages of Ani and Biju.
Solution –
Let the age of Ani and Biju be x and y years respectively.
Therefore, the age of Ani’s father, Dharam is 2x years,
And the age of Biju’s sister Cathy is years.
Case (I) : When Ani is older than Biju
The ages of Ani and Biju differ by 3 years,
x – y = 3 ——————- (i)
The ages of Cathy and Dharam differs by 30 years,
2x – = 30
4x – y = 60 ——————- (ii)
Subtracting (i) from (ii), we obtain
4x – y – (x – y) = 60 – 3
3x = 57
x = 19
Substituting x = 19 in equation (i), we obtain
19 – y = 3
y = 16
Therefore, Ani is 19 years old and Biju is 16 years old.
Case (II) : When Biju is older than Ani.
The ages of Ani and Biju differ by 3 years,
y – x = 3
– x + y = 3 ——————- (i)
The ages of Cathy and Dharam differs by 30 years,
2x – = 30
4x – y = 60 ——————- (ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we obtain
– x + y + 4x – y = 3 + 60
3x = 63
x = 21
Substituting x = 21 in equation (i), we obtain
– 21 + y = 3
y = 24
Therefore, Ani is 21 years old and Biju is 24 years old.
Thus, Ani is 19 years old and Biju is 16 years old or Ani is 21 years old and Biju is 24 years old.
2. One says, “Give me a hundred, friend! I shall then become twice as rich as you”. The other replies, “If you give me ten, I shall be six times as rich as you”. Tell me what is the amount of their (respective) capital? [From the Bijaganita of Bhaskara II]
[Hint : x + 100 = 2(y – 100), y + 10 = 6(x – 10)].
Solution –
Let the first friend have ₹ x
And the second friend has ₹ y
Using the information given in the question,
Condition 1: When second friend gives ₹ 100 to first friend;
x + 100 = 2 (y – 100)
x + 100 = 2y – 200
x – 2y = – 300 ——————- (i)
Condition 2: When first friend gives ₹ 10 to second friend;
y + 10 = 6 (x – 10)
y + 10 = 6x – 60
6x – y = 70 ——————- (ii)
Multiplying equation (ii) by 2, we obtain
12x – 2y = 140 ——————- (iii)
Subtracting equation (i) from equation (iii), we obtain
12x – 2y – (x – 2y) = 140 – (- 300)
11x = 440
x = 440/11
x = 40
Substituting x = 40 in equation (i), we obtain
40 – 2y = – 300
2y = 40 + 300
y = 340/2
y = 170
Therefore, the first friend has ₹ 40, and the second friend has ₹ 170 with them.
3. A train covered a certain distance at a uniform speed. If the train would have been 10 km/h faster, it would have taken 2 hours less than the scheduled time. And, if the train were slower by 10 km/h; it would have taken 3 hours more than the scheduled time. Find the distance covered by the train.
Solution – Let us assume the uniform speed of the train to be x km/h and the time taken to travel the given distance be t hours.
Then distance can be calculated as follows:
Distance = speed × time = xt
Thus, the distance is xt
According to the question,
Condition 1: When the train would have been 10 km/h faster, it would have taken 2 hours less than the scheduled time.
(x + 10)(t – 2) = xt
xt – 2x + 10t – 20 = xt
– 2x + 10t = 20 ——————- (i)
Condition 2: When the train would have been slower by 10 km/h, it would have taken 3 hours more than the scheduled time.
(x – 10)(t + 3) = xt
xt + 3x – 10t – 30 = xt
3x -10t = 30 ——————- (ii)
Adding equations (i) and (ii), we obtain
– 2x + 10t + 3x -10t = 20 + 30
x = 50
Substituting x = 50 in equation (i), we obtain
– 2 × 50 + 10t = 20
– 100 + 10t = 20
10t = 120
t = 120/10
t = 12
Therefore, distance = xt = 50 × 12 = 600
Hence, the distance covered by the train is 600 km.
4. The students of a class are made to stand in rows. If 3 students are extra in a row, there would be 1 row less. If 3 students are less in a row, there would be 2 rows more. Find the number of students in the class.
Solution – Let us assume the number of rows to be equal to x and the number of students in each row to be y.
Then the total number of students in the class can be calculated as follows:
Total number of students = Number of rows × Number of students in each row = xy
Using the information given in the question,
Condition 1 : If 3 students are extra in a row, there would be 1 row less
(x – 1)(y + 3) = xy
xy + 3x – y – 3 = xy
3x – y = 3 ——————- (i)
Condition 2: If 3 students are less in a row, there would be 2 rows more
(x + 2)(y – 3) = xy
xy – 3x + 2y – 6 = xy
– 3x + 2y = 6 ——————- (ii)
Adding equations (i) and (ii), we obtain
3x – y + (- 3x + 2y) = 3 + 6
y = 9
Substituting y = 9 in equation (i), we obtain
3x – 9 = 3
3x = 12
x = 4
Hence, number of students in the class, xy = 4 × 9 = 36
5. In a ∆ABC, ∠ C = 3 ∠ B = 2 (∠ A + ∠ B). Find the three angles.
Solution – Let the measurement of ∠A = x
And the measurement of ∠B = y
Using the information given in the question,
∠C = 3∠B = 2 (∠A + ∠B)
⇒ 3∠B = 2 (∠A + ∠B)
⇒ 3y = 2 ( x + y )
⇒ 3y = 2x + 2 y
⇒ 2x – y = 0 ——————- (i)
We know that the sum of the measures of all angles of a triangle is 180°. Therefore,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
⇒ ∠A + ∠B + 3∠B = 180° [∵ ∠C = 3∠B]
⇒ ∠A + 4∠B = 180
⇒ x + 4y = 180 ——————- (ii)
Multiplying equation (i) by 4, we obtain
8x – 4y = 0 ——————- (iii)
Adding equations (ii) and (iii), we obtain
x + 4y + 8x – 4y = 180 + 0
9x = 180
x = 20
Substituting x = 20 in equation (i), we obtain
2 × 20 – y = 0
y = 40
Therefore,
∠A = x = 20°
∠B = y = 40°
∠C = 3∠B = 3 × 40° = 120°
6. Draw the graphs of the equations 5x – y = 5 and 3x – y = 3. Determine the co-ordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and the y axis.
Solutions: Given,
5x – y = 5
⇒ y = 5x – 5
The solution table will be as follows.
| x | 0 | 2 |
| y | -5 | 5 |
3x – y = 3
⇒ y = 3x – 3
The solution table will be as follows.
| x | 0 | 2 |
| y | -3 | 3 |
The graphical representation of these lines will be as follows.
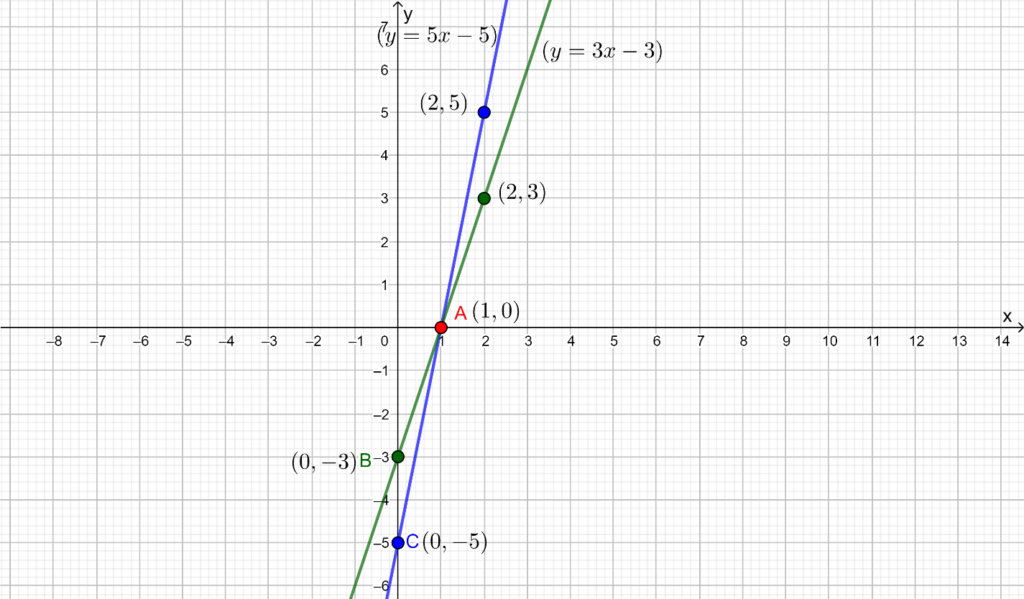
From the above graph, we can see that the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by the lines and the y-axis are (1, 0), (0, -5) and (0, -3).
7. Solve the following pair of linear equations:
(i) px + qy = p – q
qx – py = p + q
(ii) ax + by = c
bx + ay = 1 + c
(iii) x/a – y/b = 0
ax + by = a2 + b2
(iv) (a – b)x + (a + b) y = a2 – 2ab – b2
(a + b)(x + y) = a2 + b2
(v) 152x – 378y = – 74
–378x + 152y = – 604
Solutions –
(i) px + qy = p – q ———– (i)
qx – py = p + q ———– (ii)
Multiplying equation (i) by p and equation (ii) by q, we obtain
p² x + pqy = p² – pq ———– (iii)
q² x – pqy = pq + q² ———– (iv)
Adding equations (iii) and (iv), we obtain
p²x + q²x = p² + q²
(p² + q²) x = p² + q²
x = (p² + q²)/p²+ q²
x = 1
Substituting x =1 in equation (i), we obtain
p × 1 + qy = p – q
qy = – q
y = – 1
Therefore, x = 1 and y = – 1
(ii) ax + by = c ———– (i)
bx + ay = 1+ c ———– (ii)
Multiplying equation (i) by a and equation (ii) by b , we obtain
a²x + aby = ac ———– (iii)
b²x + aby = b + bc ———– (iv)
Subtracting equation (iv) from equation (iii),
(a² – b²) x = ac – bc – b
x = [c(a – b) – b]/(a² – b²)
Substituting x = [c(a – b) – b]/(a² – b²) in equation (i), we obtain
ax + by = c
a [c(a – b) – b]/(a² – b²) + by = c
[ac(a – b) – ab]/(a² – b²) + by = c
by = c – [ac(a – b) – ab]/(a² – b²)
by = [a²c – b²c – a²c + abc + ab]/(a² – b²)
by = [abc – b²c + ab]/(a² – b²)
by = [bc(a – b) + ab]/(a² – b²)
by = b [c(a – b) + a]/(a² – b²)
y = [c(a – b) + a]/(a² – b²)
Therefore, x = [c(a – b) – b]/(a² – b²) and y = [c(a – b) + a]/(a² – b²)
(iii) x/a – y/b = 0 ———– (i)
ax + by = a² + b² ———– (ii)
By solving equation (i), we obtain
x/a – y/b = 0
x = ay/b ———– (iii)
Substituting x = ay/b in equation (ii), we obtain
a (ay/b) + by = a² + b²
(a² y + b² y)/b = a² + b²
(a² + b²) y = b (a² + b²)
y = b
Substituting y = b in equation (iii), we obtain
x = (a × b)/b
x = a
Therefore, x = a and y = b
(iv) (a – b)x + (a + b) y = a² – 2ab – b² ———– (i)
(a + b)(x + y) = a² + b² ———– (ii)
By solving equation (ii), we obtain
(a + b)(x + y) = a² + b²
(a + b)x + (a + b) y = a² + b² ———– (iii)
Subtracting equation (iii) from (i), we obtain
(a – b)x – (a + b)x = (a² – 2ab – b²) – (a² + b²)
[(a – b) – (a + b)] x = a² – 2ab – b² – a² – b²
[a – b – a – b] x = -2ab – 2b²
-2bx = -2b (a + b)
x = (a + b)
Substituting x = (a + b) in equation (i), we obtain
(a – b)(a + b) + (a + b) y = a² – 2ab – b²
(a² – b²) + (a + b) y = a² – 2ab – b²
(a + b) y = a² – 2ab – b² – (a² – b²)
(a + b) y = a² – 2ab – b² – a² + b²
y = -2ab/(a + b)
(v) 152x – 378y = -74 ———– (i)
– 378x + 152y = – 604 ———– (ii)
Adding equations (i) and (ii), we obtain
-226x – 226y = – 678
-226( x + y ) = – 678
x + y = 3 ———– (iii)
Subtracting equation (ii) from (i), we obtain
530x – 530y = 530
530 ( x – y ) = 530
x – y = 1 ———– (iv)
Adding equations (iii) and (iv), we obtain
2x = 4
x = 2
Substituting x = 2 in equation (iii), we obtain
2 + y = 3
y = 1
Therefore, x = 2 and y = 1
8. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral (see Fig. 3.7). Find the angles of the cyclic quadrilateral.
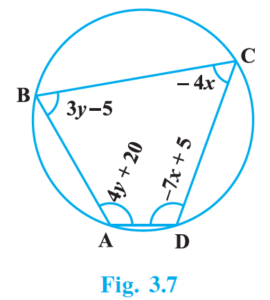
Solution –
Given that ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral.
As we know, the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary.
So,
∠A + ∠C = 180
4y + 20 + (-4x) = 180
-4x + 4y = 160
⇒ -x + y = 40 ———– (i)
And
∠B + ∠D = 180
3y – 5 + (-7x + 5) = 180
⇒ -7x + 3y = 180 ———– (ii)
Equation (ii) – 3 × (i),
-7x + 3y – (-3x + 3y) = 180 – 120
-4x = 60
x = -15
Substituting x = -15 in equation (i), we get;
-(-15) + y = 40
y = 40 – 15 = 25
Therefore, x = -15 and y = 25.

Leave a Reply