NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science (Geography – Contemporary India – I)
The NCERT Solutions in English Language for Class 9 Social Science (Geography – Contemporary India – I) Chapter – 3 (Drainage) has been provided here to help the students in solving the questions from this exercise.
Chapter – 3 (Drainage)
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) In which of the following states is the Wular lake located?
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Punjab
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Jammu and Kashmir
Answer – (d) Jammu and Kashmir
(ii) The river Narmada has its source at
(a) Satpura
(b) Amarkantak
(c) Brahmagiri
(d) Slopes of the Western Ghat
Answer – (b) Amarkantak
(iii) Which one of the following lakes is a saltwater lake?
(a) Sambhar
(b) Wular
(c) Dal
(d) Gobind Sagar
Answer – (a) Sambhar
(iv) Which one of the following is the longest river in Peninsular India?
(a) Narmada
(b) Godavari
(c) Krishna
(d) Mahanadi
Answer – (b) Godavari
(v) Which one amongst the following rivers flows through a rift valley?
(a) Mahanadi
(b) Krishna
(c) Tungabhadra
(d) Tapi
Answer – (d) Tapi
2. Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) What is meant by a water divide? Give an example.
Answer – Any upland or a mountain separating two adjoining drainage basins is known as water divide. An example of water divide is the Western Ghats.
(ii) Which is the largest river basin in India?
Answer – The Ganga River Basin is the largest river basin in India.
(iii) Where do the rivers Indus and Ganga have their origin?
Answer –
Indus River origin – Near Manasarovar Lake, Tibet
Ganga River origin – Gangotri glacier in Uttaranchal
(iv) Name the two headstreams of the Ganga. Where do they meet to form the Ganga?
Answer – The two headstreams of the Ganga are Alaknanda and Bhagirathi. They both meet to form Ganga at Devprayag.
(v) Why does the Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part have less silt, despite a longer course?
Answer – The Brahmaputra river, which is known as Tsangpo in Tibet, carries a smaller volume of water and less silt as it is a cold and dry area. But once it enters India, Brahmaputra is fed by heavy rains, and it carries lot of water and silt.
(vi) Which two Peninsular rivers flow through a trough?
Answer – The two rivers that flow through troughs are Narmada and Tapi. They form estuaries while entering the sea.
(vii) State some economic benefits of rivers and lakes.
Answer – Economic benefits of rivers and lakes are as follows
(i) They provide fresh water for drinking and other domestic purposes.
(ii) The water is useful for irrigation in agriculture as well as for industrial processes in manufacturing.
(iii) Deltas of rivers provide fertile soil for increasing agricultural yield.
(iv) They are used for generation of hydroelectricity.
(v) They provide economical inland transport facilities.
(vi) They provide fresh water fisheries.
(vii) Rivers help to carry away effluents and sewage.
3. Below are given names of a few lakes of India. Group them under two categories – natural and created by human beings.
| (a) Wular | (b) Dal |
| (c) Nainital | (d) Bhimtal |
| (e) Gobind Sagar | (f) Loktak |
| (g) Barapani | (h) Chilika |
| (i) Sambhar | (j) Rana Pratap Sagar |
| (k) Nizam Sagar | (l) Pulicat |
| (m) Nagarjuna Sagar | (n) Hirakund |
Answer –
Natural Lakes – (a) Wular, (b) Dal, (c) Nainital, (d) Bhimtal, (f) Loktal, (g) Barapani, (h) Chilika, (i) Sambhar, (l) Pulicat
Human-made Lakes – (e) Gobind Sagar, (j) Rana Pratap Sagar, (k) Nizam Sagar, (m) Nagarjuan Sagar, (n) Hirakud
4. Discuss the significant difference between the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers.
Answer –
| Himalayan Rivers | Peninsular Rivers |
| Originate from Himalayas | Originate in the Western Ghats |
| These are perennial rivers. |
These are seasonal rivers. |
| They carry a lot silt and sand. | They carry very less or no silt and sand. |
| Their drainage basins are large. | Their drainage basins are small. |
| These rivers form big deltas. | They form small deltas. |
| They are useful for irrigation, cultivation and navigation. | They are seasonal and flow over rocky areas and are not useful for cultivation and navigation. |
5. Compare the east-flowing and the west-flowing rivers of the Peninsular plateau.
Answer – The difference between east flowing rivers and west flowing rivers are.
| West flowing rivers | East flowing rivers |
| These rivers originate from the Western Ghats and flow eastwards. | These rivers originate from the Western Ghats and flow eastwards. |
| These rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal. |
These rivers flow into the Arabian Sea. |
| These rivers from deltas at their mouths. | These rivers form estuaries at their mouths. |
| They carry larger amount of water. | They carry a lesser amount of water. |
| Examples are Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishana and Kaveri. | Examples are Narmada and Tapi. |
6. Why are rivers important for the country’s economy?
Answer – Rivers are important for the country’s economy because water from the rivers is a basic natural resource essential for various human activities. These are —
1. The rivers provide water for irrigation.
2. They provide fertility to the soil.
3. They are useful for navigation.
4. They help to generate hydro-electricity.
5. They help to develop tourism.
6. They provide water for various domestic uses.
7. They provide livelihood to fishermen.
8. They help to moderate the climate and environment of nearby areas.
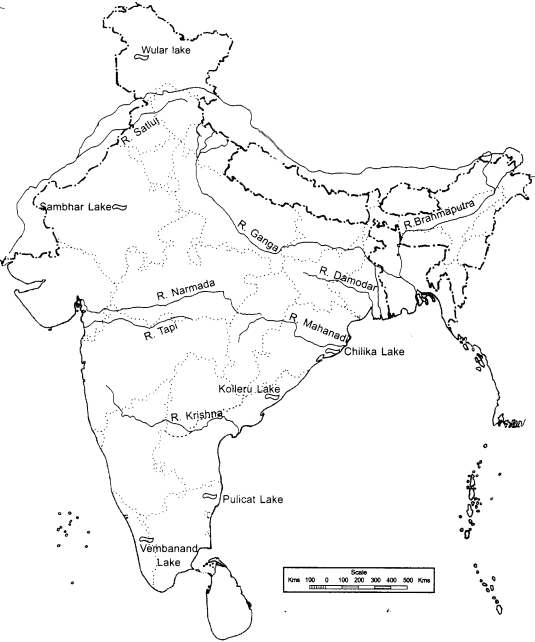
MAP SKILLS
(i) On an outline map of India mark and label the following rivers: Ganga, Satluj, Damodar, Krishna, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, and Brahmaputra.
(ii) On an outline map of India mark and label the following lakes: Chilika, Sambhar, Wular, Pulicat, Kolleru.
Answer –
Project / Activity
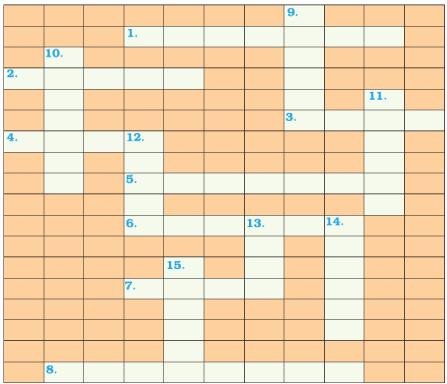
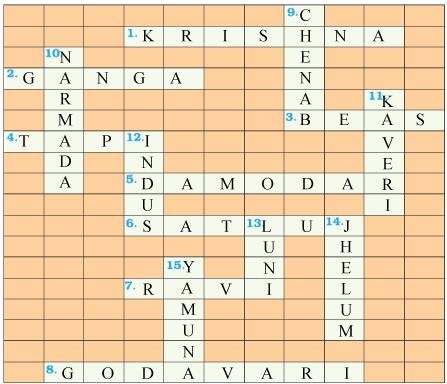
Solve this crossword puzzle with the help of given clues.
Across
1. Nagarjuna Sagar is a river valley project. Name the river?
2. The longest river of India.
3. The river which originates from a place known as Beas Kund.
4. The river which rises in the Betul district of MP and flows westwards.
5. The river which was known as the “Sorrow” of West Bengal.
6. The river on which the reservoir for Indira Gandhi Canal has been built.
7. The river whose source lies near Rohtang Pass.
8. The longest river of Peninsular India?
Down
9. A tributary of Indus originating from Himachal Pradesh.
10. The river flowing through fault, drains into the Arabian Sea.
11. A river of south India, which receives rainwater both in summer and winter.
12. A river which flows through Ladakh, Gilgit and Pakistan.
13. An important river of the Indian desert.
14. The river which joins Chenab in Pakistan.
15. A river which rises at Yamunotri glacier.
Answer –

Leave a Reply